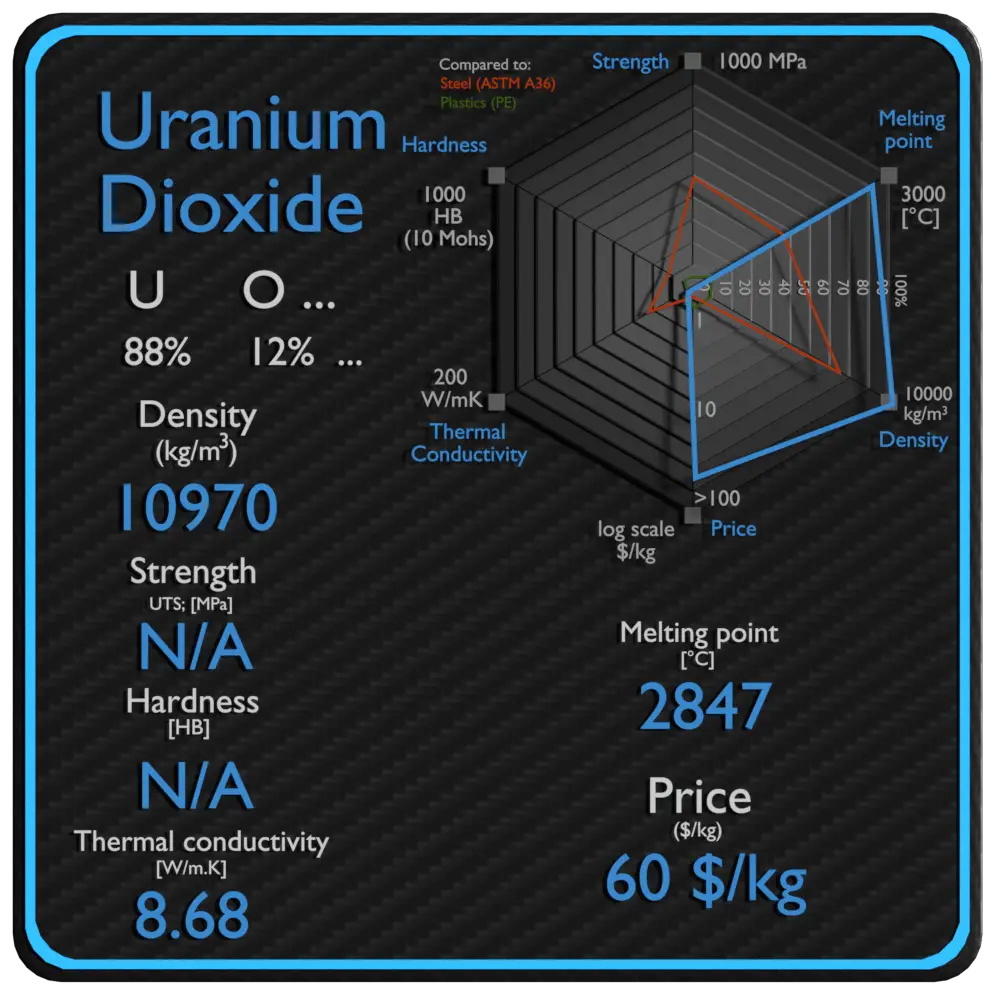
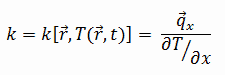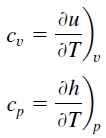About Uranium Dioxide
Uranium dioxide is a ceramic refractory uranium compound, in many cases used as a nuclear fuel. Most of LWRs use the uranium fuel, which is in the form of uranium dioxide (chemically UO2). Uranium dioxide is a black semiconducting solid with very low thermal conductivity. On the other hand the uranium dioxide has very high melting point and has well known behavior. Uranium dioxide has significantly lower density than uranium in the metal form. Uranium dioxide has a density of 10.97 g/cm3, but this value may vary with fuel burnup, because at low burnup densification of pellets can occurs and at higher burnup swelling occurs.
Summary
| Name | Uranium Dioxide |
| Phase at STP | solid |
| Density | 10970 kg/m3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | N/A |
| Yield Strength | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | N/A |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A |
| Melting Point | 2847 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8.68 W/mK |
| Heat Capacity | 235 J/g K |
| Price | 60 $/kg |
Composition of Uranium Dioxide
The UO2 is pressed into pellets, these pellets are then sintered into the solid cylinder (with a height, and diameter of about 1 centimeter, the height being greater than the diameter).
Applications of Uranium Dioxide

Most of PWRs use the uranium fuel, which is in the form of uranium dioxide.
Thermal Properties of Uranium Dioxide
Uranium Dioxide – Melting Point
Melting point of Uranium Dioxide is 2847 °C.
Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. For various chemical compounds and alloys, it is difficult to define the melting point, since they are usually a mixture of various chemical elements.
Uranium Dioxide – Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity of Uranium Dioxide is 8.68 W/(m·K).
The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.K. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Note that Fourier’s law applies for all matter, regardless of its state (solid, liquid, or gas), therefore, it is also defined for liquids and gases.
The thermal conductivity of most liquids and solids varies with temperature. For vapors, it also depends upon pressure. In general:
Most materials are very nearly homogeneous, therefore we can usually write k = k (T). Similar definitions are associated with thermal conductivities in the y- and z-directions (ky, kz), but for an isotropic material the thermal conductivity is independent of the direction of transfer, kx = ky = kz = k.
Uranium Dioxide – Specific Heat
Specific heat of Uranium Dioxide is 235 J/g K.
Specific heat, or specific heat capacity, is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics. The intensive properties cv and cp are defined for pure, simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of the internal energy u(T, v) and enthalpy h(T, p), respectively:
where the subscripts v and p denote the variables held fixed during differentiation. The properties cv and cp are referred to as specific heats (or heat capacities) because under certain special conditions they relate the temperature change of a system to the amount of energy added by heat transfer. Their SI units are J/kg K or J/mol K.
Properties and prices of other materials
material-table-in-8k-resolution