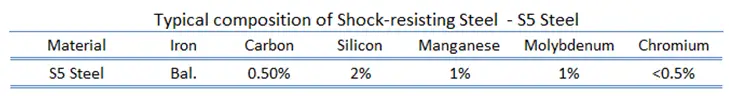
Shock-resisting steels are a specialized class of tool steels with very high impact toughness and relatively low abrasion resistance and can attain relatively high hardness (HRC 58/60). Shock-resisting steels are designated as Group S steels according to the AISI classification system. The high shock resistance and good hardenability are provided by chromium-tungsten, silicon-molybdenum, silicon-manganese alloying. The principal alloying elements in shock-resisting steels, also called group S steels, are manganese, silicon, chromium, tungsten, and molybdenum, in various combinations. A low carbon content is required for the necessary toughness (approximately 0.5% carbon). Type S1, S5, and S6 steels are oil quenched and type S2 steels are water quenched.
Group S steels are used primarily for chisels, rivet sets, punches, springs, dies for forging, and punches, and other applications requiring high toughness and resistance to shock loading.
We hope, this article, Composition of Shock-resisting Steel, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.