As was written, a crystalline material is one in which the atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances—that is, long-range order exists, such that upon solidification, the atoms will position themselves in a repetitive three-dimensional pattern, in which each atom is bonded to its nearest neighbor atoms. But reality is different, real crystals are never perfect. There are always defects. The influence of these defects is not always adverse, and often specific characteristics are deliberately fashioned by the introduction of controlled amounts or numbers of particular defects.
Vacancy
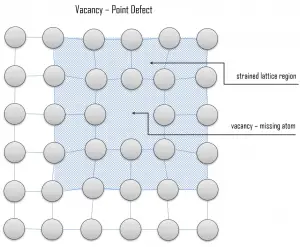 Vacancy defects result from a missing atom in a lattice position. The stability of the surrounding crystal structure guarantees that the neighboring atoms will not simply collapse around the vacancy. The vacancy type of defect can result from imperfect packing during the crystallization process, or it may be due to increased thermal vibrations of the atoms brought about by elevated temperature. All crystalline solids contain vacancies, and, in fact, it is not possible to create such a material that is free of these defects. A vacancy (or pair of vacancies in an ionic solid) is sometimes called a Schottky defect. This point defect forms when oppositely charged ions leave their lattice sites, creating vacancies. These vacancies are formed in stoichiometric units, to maintain an overall neutral charge in the ionic solid.
Vacancy defects result from a missing atom in a lattice position. The stability of the surrounding crystal structure guarantees that the neighboring atoms will not simply collapse around the vacancy. The vacancy type of defect can result from imperfect packing during the crystallization process, or it may be due to increased thermal vibrations of the atoms brought about by elevated temperature. All crystalline solids contain vacancies, and, in fact, it is not possible to create such a material that is free of these defects. A vacancy (or pair of vacancies in an ionic solid) is sometimes called a Schottky defect. This point defect forms when oppositely charged ions leave their lattice sites, creating vacancies. These vacancies are formed in stoichiometric units, to maintain an overall neutral charge in the ionic solid.
We hope, this article, Vacancy – Crystallographic Defects, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.