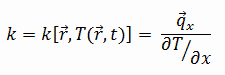Nickel silver, known also as German silver, nickel brass or alpacca, is a copper alloy with nickel and often zinc. The usual formulation is 60% copper, 20% nickel and 20% zinc. For example the alloy C75700 contains 63.5 to 66.5% of Cu, 11.0 to 13.0% of Ni, 0.05% Pb max, 0.25% Fe max, 0.5% Mn max, and balance of Zn. UNS C75700 nickel silver 65-12 copper alloy has good corrosion and tarnish-resistance, and high formability. Nickel silver is named due to its silvery appearance, but it contains no elemental silver unless plated.
Nickel silver alloys are used for decorative applications, jewellery, model making, musical instruments (e.g., flutes, clarinets), flutes ball point refills, screws, rivets and fishing rods, test probes.
Thermal Properties of Nickel Silver
Thermal properties of materials refer to the response of materials to changes in their temperature and to the application of heat. As a solid absorbs energy in the form of heat, its temperature rises and its dimensions increase. But different materials react to the application of heat differently.
Heat capacity, thermal expansion, and thermal conductivity are properties that are often critical in the practical use of solids.
Melting Point of Nickel Silver
Melting point of nickel silver – UNS C75700 is around 1040°C.
In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium.
Thermal Conductivity of Nickel Silver
The thermal conductivity of nickel silver – UNS C75700 is 40 W/(m.K).
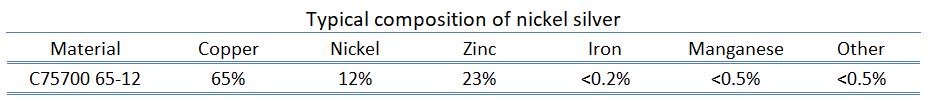
The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.K. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Note that Fourier’s law applies for all matter, regardless of its state (solid, liquid, or gas), therefore, it is also defined for liquids and gases.
The thermal conductivity of most liquids and solids varies with temperature. For vapors, it also depends upon pressure. In general:
Most materials are very nearly homogeneous, therefore we can usually write k = k (T). Similar definitions are associated with thermal conductivities in the y- and z-directions (ky, kz), but for an isotropic material the thermal conductivity is independent of the direction of transfer, kx = ky = kz = k.
We hope, this article, Thermal Properties of Nickel Silver, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.