Cementite (Fe3C) is a metastable compound, and under some circumstances it can be made to dissociate or decompose to form α-ferrite and graphite, according to the reaction:
Fe3C → 3Fe (α) + C (graphite)
The decomposition time is long and it will take much longer than the service life of the application at room temperature. Some other factors (high temperatures and addition of certain alloying elements for instance) can affect this decomposition as they promote graphite formation.
Cementite in its pure form is a ceramic and it is hard and brittle which makes it suitable for strengthening steels. Its mechanical properties are a function of its microstructure, which depends upon how it is mixed with ferrite.
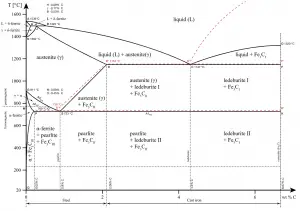
In the iron–carbon system (i.e. plain-carbon steels and cast irons) it is a common constituent because ferrite can contain at most 0.02wt% of uncombined carbon. Therefore, in carbon steels and cast irons that are slowly cooled, a portion of the carbon is in the form of cementite.
Cementite forms directly from the melt in the case of white cast iron. With a lower silicon content (containing less than 1.0 wt% Si – graphitizing agent) and faster cooling rate, the carbon in cast iron precipitates out of the melt as the metastable phase cementite, Fe3C, rather than graphite. The product of this solidification is known as white cast iron (also known as chilled irons).
In carbon steel, cementite precipitates from austenite as austenite transforms to ferrite on slow cooling, or from martensite during tempering. An intimate mixture with ferrite, the other product of austenite, forms a lamellar structure called pearlite.
In cast irons, graphite formation is promoted by the presence of silicon in concentrations greater than about 1 wt%. Also, slower cooling rates during solidification favor graphitization (the formation of graphite).
Other Common Phases in Steels and Irons
Heat treatment of steels requires an understanding of both the equilibrium phases and the metastable phases that occur during heating and/or cooling. For steels, the stable equilibrium phases include:
- Ferrite. Ferrite or α-ferrite is a body-centered cubic structure phase of iron which exists below temperatures of 912°C for low concentrations of carbon in iron. α-ferrite can only dissolve up to 0.02 percent of carbon at 727°C. This is because of the configuration of the iron lattice which forms a BCC crystal structure. The primary phase of low-carbon or mild steel and most cast irons at room temperature is ferromagnetic α-Fe.
- Austenite. Austenite, also known as gamma-phase iron (γ-Fe), is a non-magnetic face-centered cubic structure phase of iron. Austenite in iron-carbon alloys is generally only present above the critical eutectoid temperature (723°C), and below 1500°C, depending on carbon content. However, it can be retained to room temperature by alloy additions such as nickel or manganese. Carbon plays an important role in heat treatment, because it expands the temperature range of austenite stability. Higher carbon content lowers the temperature needed to austenitize steel—such that iron atoms rearrange themselves to form an fcc lattice structure. Austenite is present in the most commonly used type of stainless steel, which are very well known for their corrosion resistance.
- Graphite. Adding a small amount of non-metallic carbon to iron trades its great ductility for the greater strength.
- Cementite. Cementite (Fe3C) is a metastable compound, and under some circumstances it can be made to dissociate or decompose to form α-ferrite and graphite, according to the reaction: Fe3C → 3Fe (α) + C (graphite). Cementite in its pure form is a ceramic and it is hard and brittle which makes it suitable for strengthening steels. Its mechanical properties are a function of its microstructure, which depends upon how it is mixed with ferrite.
The metastable phases are:
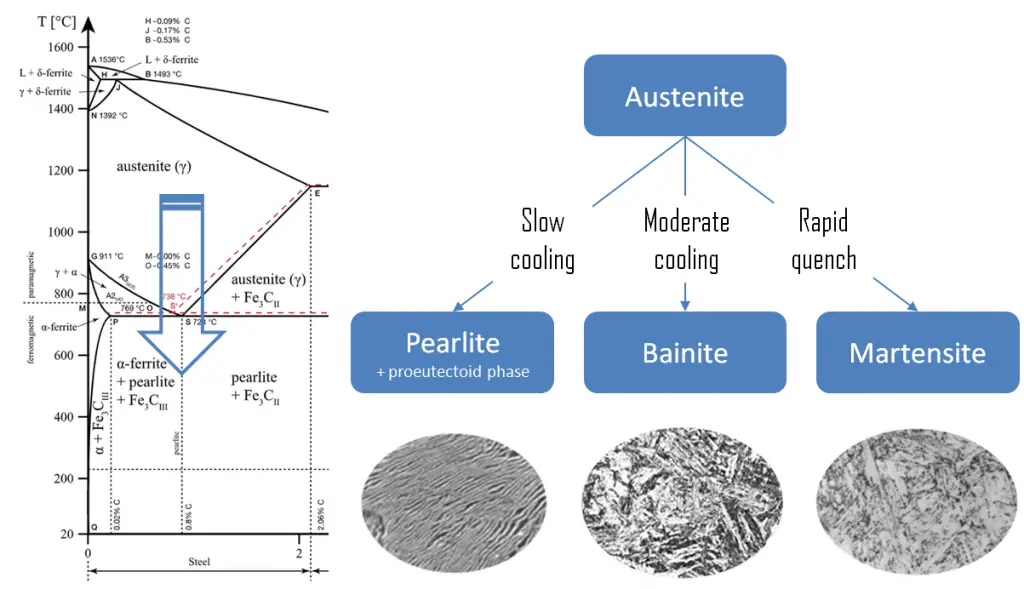 Pearlite. In metallurgy, pearlite is a layered metallic structure of two-phases, which compose of alternating layers of ferrite (87.5 wt%) and cementite (12.5 wt%) that occurs in some steels and cast irons. It is named for its resemblance to mother of pearl.
Pearlite. In metallurgy, pearlite is a layered metallic structure of two-phases, which compose of alternating layers of ferrite (87.5 wt%) and cementite (12.5 wt%) that occurs in some steels and cast irons. It is named for its resemblance to mother of pearl.- Martensite. Martensite is a very hard metastable structure with a body-centered tetragonal (BCT) crystal structure. Martensite is formed in steels when the cooling rate from austenite is at such a high rate that carbon atoms do not have time to diffuse out of the crystal structure in large enough quantities to form cementite (Fe3C).
- Bainite. Bainite is a plate-like microstructure that forms in steels from austenite when cooling rates are not rapid
enough to produce martensite but are still fast enough so that carbon does not have enough time to diffuse to form pearlite. Bainitic steels are generally stronger and harder than pearlitic steels; yet they exhibit a desirable combination of strength and ductility.
We hope, this article, Cementite – Fe3C, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.