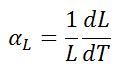Invar is a group of low thermal expansion nickel-iron alloys consisting primarily of nickel and iron (e.g. FeNi36). The name Invar comes from the word invariable, referring to its relative lack of expansion or contraction with temperature changes. The Invar alloy is ductile and easily weldable, and machinability is similar to austenitic stainless steel.
Invar is used where high dimensional stability is required, such as precision instruments, clocks . Alloys with low coefficients of expansion form the essential part of bimetals and thermostats. Invar itself is still used today in vast numbers of household appliances, from electric irons and toasters to gas cookers and fire safety cutoffs. Invars can be also used in glass-to-metal seals, and electronic and radio components. Almost all variable condensers are made of Invar. Struts on jet engines are made of Invar to ensure rigidity with temperature changes.
Thermal Expansion Coefficient of Invar
Linear coefficient of thermal expansion of invar – FeNi36 at 25 to 105°C is about 1.2 x 10-6 K-1 (1.2 ppm/°C).
Linear coefficient of thermal expansion of constantan at 25 to 105°C is 14.9 x 10-6 K-1.
Thermal expansion is generally the tendency of matter to change its dimensions in response to a change in temperature. It is usually expressed as a fractional change in length or volume per unit temperature change. Thermal expansion is common for solids, liquids and for gases. Unlike gases or liquids, solid materials tend to keep their shape when undergoing thermal expansion. A linear expansion coefficient is usually employed in describing the expansion of a solid, while a volume expansion coefficient is more useful for a liquid or a gas.
The linear thermal expansion coefficient is defined as:
where L is a particular length measurement and dL/dT is the rate of change of that linear dimension per unit change in temperature.
We hope, this article, Invar – Properties and Uses, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.