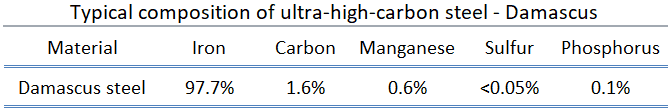
Ultra-high-carbon steel has approximately 1.25–2.0% carbon content. Steels that can be tempered to great hardness. This grade of steel could be used for hard steel products, such as truck springs, metal cutting tools and other special purposes like (non-industrial-purpose) knives, axles or punches. Most steels with more than 2.5% carbon content are made using powder metallurgy.
Ultra-high carbon steels (i.e., steels containing between 1 and 2.0% C and now known as UHCS) have extreme strength, sharpness and resilience. The early use of steel compositions containing carbon contents above the eutectoid level is found in ancient weapons from around the world. For example, both Damascus and Japanese sword steels are hypereutectoid steels. The room temperature mechanical properties of the ultra-high-carbon steels exhibited a yield strength of 900 MPa and an ultimate strength of 1100 MPa. This is a remarkable combination of strength and ductility and confirms the general statements made about the malleability of ancient Damascus steels.
Properties of Ultra-high-carbon Steel – Damascus Steel
Material properties are intensive properties, that means they are independent of the amount of mass and may vary from place to place within the system at any moment. The basis of materials science involves studying the structure of materials, and relating them to their properties (mechanical, electrical etc.). Once a materials scientist knows about this structure-property correlation, they can then go on to study the relative performance of a material in a given application. The major determinants of the structure of a material and thus of its properties are its constituent chemical elements and the way in which it has been processed into its final form.
Mechanical Properties of Ultra-high-carbon Steel – Damascus Steel
Materials are frequently chosen for various applications because they have desirable combinations of mechanical characteristics. For structural applications, material properties are crucial and engineers must take them into account.
Strength of Ultra-high-carbon Steel – Damascus Steel
In mechanics of materials, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. Strength of materials basically considers the relationship between the external loads applied to a material and the resulting deformation or change in material dimensions. Strength of a material is its ability to withstand this applied load without failure or plastic deformation.
Ultimate Tensile Strength
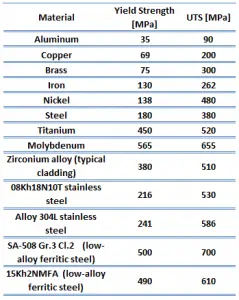
Ultimate tensile strength of ultra-high-carbon steel is 1100 MPa.
 The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension. Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to “tensile strength” or even to “the ultimate.” If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result. Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals). When a ductile material reaches its ultimate strength, it experiences necking where the cross-sectional area reduces locally. The stress-strain curve contains no higher stress than the ultimate strength. Even though deformations can continue to increase, the stress usually decreases after the ultimate strength has been achieved. It is an intensive property; therefore its value does not depend on the size of the test specimen. However, it is dependent on other factors, such as the preparation of the specimen, the presence or otherwise of surface defects, and the temperature of the test environment and material. Ultimate tensile strengths vary from 50 MPa for an aluminum to as high as 3000 MPa for very high-strength steels.
The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension. Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to “tensile strength” or even to “the ultimate.” If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result. Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals). When a ductile material reaches its ultimate strength, it experiences necking where the cross-sectional area reduces locally. The stress-strain curve contains no higher stress than the ultimate strength. Even though deformations can continue to increase, the stress usually decreases after the ultimate strength has been achieved. It is an intensive property; therefore its value does not depend on the size of the test specimen. However, it is dependent on other factors, such as the preparation of the specimen, the presence or otherwise of surface defects, and the temperature of the test environment and material. Ultimate tensile strengths vary from 50 MPa for an aluminum to as high as 3000 MPa for very high-strength steels.
Yield Strength
Yield strength of ultra-high-carbon steel is 800 MPa.
The yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior. Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins. Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible. Some steels and other materials exhibit a behaviour termed a yield point phenomenon. Yield strengths vary from 35 MPa for a low-strength aluminum to greater than 1400 MPa for very high-strength steels.
Hardness of Ultra-high-carbon Steel – Damascus Steel
Rockwell hardness of Damascus steel depends on the current type of the steel, but it may be approximately 62-64 HRC Rockwell.
Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). The minor load establishes the zero position. The major load is applied, then removed while still maintaining the minor load. The difference between depth of penetration before and after application of the major load is used to calculate the Rockwell hardness number. That is, the penetration depth and hardness are inversely proportional. The chief advantage of Rockwell hardness is its ability to display hardness values directly. The result is a dimensionless number noted as HRA, HRB, HRC, etc., where the last letter is the respective Rockwell scale.
We hope, this article, Ultra-high-carbon Steel – Damascus Steel, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.