Source: chemwiki.ucdavis.edu
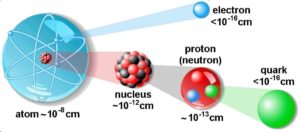
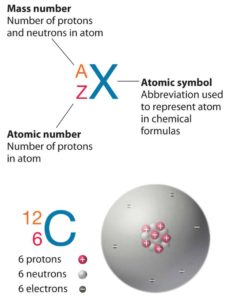
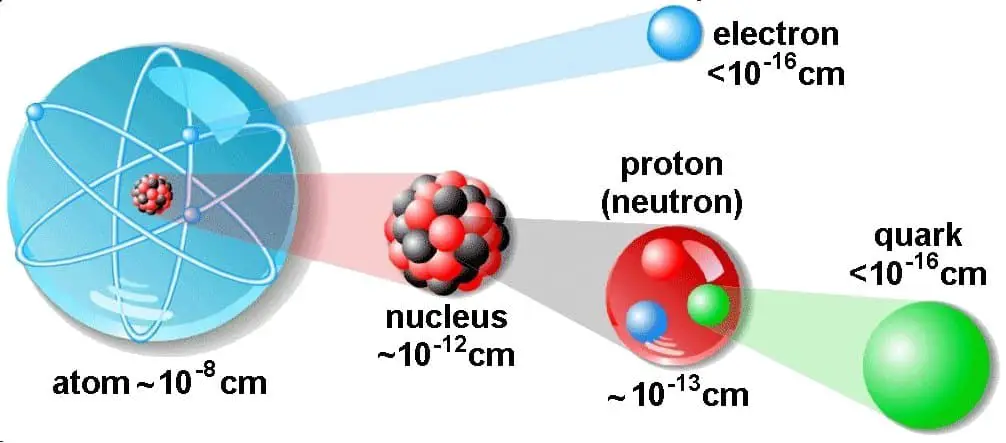
The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus. It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements.
Hydrogen (H), for example , consist of one electron and one proton. The number of neutrons in a nucleus is known as the neutron number and is given the symbol N. The total number of nucleons, that is, protons and neutrons in a nucleus, is equal to Z + N = A, where A is called the atomic mass number. The various species of atoms whose nuclei contain particular numbers of protons and neutrons are called nuclides. Each nuclide is denoted by chemical symbol of the element (this specifies Z) with tha atomic mass number as supescript.
Thus the symbol 1H refers to the nuclide of hydrogen with a single proton as nucleus. 2H is the hydrogen nuclide with a neutron as well as a proton in the nucleus (2H is also called deuterium or heavy hydrogen). Atoms such as 1H, 2H whose nuclei contain the same number of protons but different number of neutrons (different A) are known as isotopes. Uranium, for instance, has three isotopes occuring in nature – 238U, 235U and 234U. The stable isotopes (plus a few of the unstable isotopes) are the atoms that are found in the naturally occuring elements in nature. However, they are not found in equal amounts. Some isotopes of a given element are more abundant than others. For example 99,27% of naturally occuring uranium atoms are the isotope 238U, 0,72% are the isotope 235U and 0,0055% are the isotope 234U. Exact structure of atoms is described by Atomic Theory and Theory of Nuclear Structure.
- Atomic Theory. Atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning “uncuttable”. Today it is known that also atoms are divisible. Atomic Theory consist of many models and discoveries, which gradually formed this theory.
- Theory of Nuclear Structure. Understanding the structure of the atomic nucleus is one of the central challenges in modern nuclear physics.
We hope, this article, Atomic and Nuclear Structure, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.