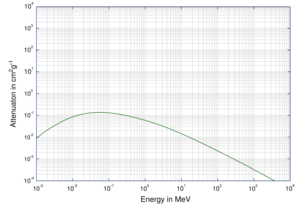
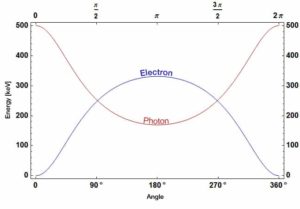
Compton Scattering
Compton Scattering – Cross-Sections
The probability of Compton scattering per one interaction with an atom increases linearly with atomic number Z, because it depends on the number of electrons, which are available for scattering in the target atom. The angular distribution of photons scattered from a single free electron is described by the Klein-Nishina formula: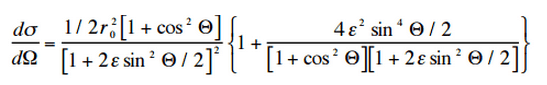 where ε = E0/mec2 and r0 is the “classical radius of the electron” equal to about 2.8 x 10-13 cm. The formula gives the probability of scattering a photon into the solid angle element dΩ = 2π sin Θ dΘ when the incident energy is E0.
where ε = E0/mec2 and r0 is the “classical radius of the electron” equal to about 2.8 x 10-13 cm. The formula gives the probability of scattering a photon into the solid angle element dΩ = 2π sin Θ dΘ when the incident energy is E0.
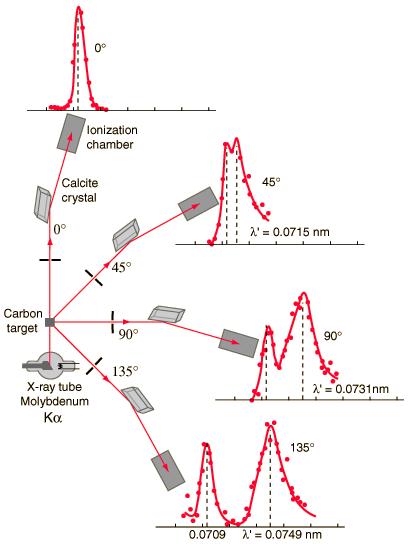
Source: hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/
We hope, this article, Cross-Section of Compton Scattering, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.