Photoelectric Effect
- The photoelectric effect dominates at low-energies of gamma rays.
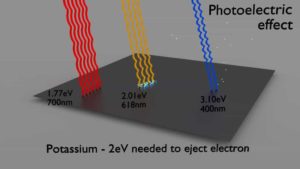
- The photoelectric effect leads to the emission of photoelectrons from matter when light (photons) shines upon them.
- The maximum energy an electron can receive in any one interaction is hν.
- Electrons are only emitted by the photoelectric effect if photon reaches or exceeds a threshold energy.
- A free electron (e.g. from atomic cloud) cannot absorb entire energy of the incident photon. This is a result of the need to conserve both momentum and energy.
- The cross-section for the emission of n=1 (K-shell) photoelectrons is higher than that of n=2 (L-shell) photoelectrons. This is a result of the need to conserve momentum and energy.
Definition of Photoelectric effect
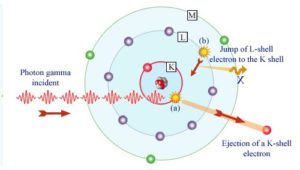
In the photoelectric effect, a photon undergoes an interaction with an electron which is bound in an atom. In this interaction the incident photon completely disappears and an energetic photoelectron is ejected by the atom from one of its bound shells. The kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectron (Ee) is equal to the incident photon energy (hν) minus the binding energy of the photoelectron in its original shell (Eb).
Ee=hν-Eb
Therefore photoelectrons are only emitted by the photoelectric effect if photon reaches or exceeds a threshold energy – the binding energy of the electron – the work function of the material. For gamma rays with energies of more than hundreds keV, the photoelectron carries off the majority of the incident photon energy – hν.Following a photoelectric interaction, an ionized absorber atom is created with a vacancy in one of its bound shells. This vacancy is will be quickly filled by an electron from a shell with a lower binding energy (other shells) or through capture of a free electron from the material. The rearrangement of electrons from other shells creates another vacancy, which, in turn, is filled by an electron from an even lower binding energy shell. Therefore a cascade of more characteristic X-rays can be also generated. The probability of characteristic x-ray emission decreases as the atomic number of the absorber decreases. Sometimes , the emission of an Auger electron occurs.
We hope, this article, Definition of Photoelectric Effect, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.