Source: scienceblogs.com
A free neutron is a neutron that is not bounded in a nucleus. The free neutron is, unlike a bounded neutron, subject to radioactive beta decay.
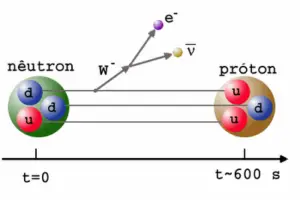
It decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino (the antimatter counterpart of the neutrino, a particle with no charge and little or no mass). A free neutron will decay with a half-life of about 611 seconds (10.3 minutes). This decay involves the weak interaction and is associated with a quark transformation (a down quark is converted to an up quark). The decay of the neutron is a good example of the observations which led to the discovery of the neutrino. Because it decays in this manner, the neutron does not exist in nature in its free state, except among other highly energetic particles in cosmic rays. Since free neutrons are electrically neutral, they pass through the electrical fields within atoms without any interaction and they are interacting with matter almost exclusively through relatively rare collisions with atomic nuclei.
We hope, this article, Free Neutron, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.