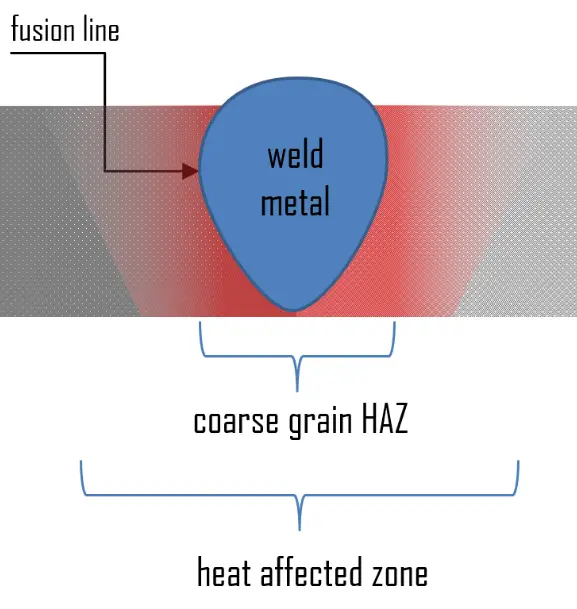
 In this section we will focus on fusion welding, which is more common than solid-state welding. Fusion welding is used in the manufacture of many everyday items including airplanes, cars, and structures. By using a heat source with sufficient power it is possible to fuse through a complete section of very thick plate. The weld pool produced is difficult to control and the heat affected zone (HAZ) of such welds has a relatively coarse grain, adversely affecting the mechanical properties of the steel. The heat-affected zone (HAZ) is a ring surrounding the weld in which the temperature of the welding process, combined with the stresses of uneven heating and cooling, alter the heat-treatment properties of the alloy. The effects of welding on the material surrounding the weld can be detrimental—depending on the materials used and the heat input of the welding process used, the HAZ can be of varying size and strength. In the weld pool, heat is transported by means of convection and conduction.
In this section we will focus on fusion welding, which is more common than solid-state welding. Fusion welding is used in the manufacture of many everyday items including airplanes, cars, and structures. By using a heat source with sufficient power it is possible to fuse through a complete section of very thick plate. The weld pool produced is difficult to control and the heat affected zone (HAZ) of such welds has a relatively coarse grain, adversely affecting the mechanical properties of the steel. The heat-affected zone (HAZ) is a ring surrounding the weld in which the temperature of the welding process, combined with the stresses of uneven heating and cooling, alter the heat-treatment properties of the alloy. The effects of welding on the material surrounding the weld can be detrimental—depending on the materials used and the heat input of the welding process used, the HAZ can be of varying size and strength. In the weld pool, heat is transported by means of convection and conduction.
An understanding of heat transfer is important in the production of welds inasmuch as the properties of a weldment are controlled by its geometry and by the composition and structure of the materials being welded.
We hope, this article, Heat-affected Zone – HAZ, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.