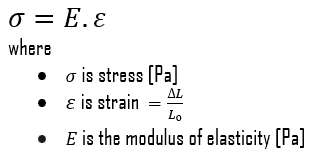High purity aluminium is a soft material with the ultimate strength of approximately 10 MPa, which limits its usability in industrial applications. Aluminium of commercial purity (99-99.6%) becomes harder and stronger due to the presence of impurities, especially of Si and Fe. But when alloyed, aluminium alloys are heat treatable, which significantly changes theri mechanical properties.
 Aluminium alloys are based on aluminium, in which the main alloying elements are Cu, Mn, Si, Mg, Mg+Si, Zn. Aluminium alloy compositions are registered with The Aluminum Association. The aluminium alloys are divided into 9 families (Al1xxx to Al9xxx). The different families of alloys and the major alloying elements are:
Aluminium alloys are based on aluminium, in which the main alloying elements are Cu, Mn, Si, Mg, Mg+Si, Zn. Aluminium alloy compositions are registered with The Aluminum Association. The aluminium alloys are divided into 9 families (Al1xxx to Al9xxx). The different families of alloys and the major alloying elements are:
- 1xxx: no alloying elements
- 2xxx: Copper
- 3xxx: Manganese
- 4xxx: Silicon
- 5xxx: Magnesium
- 6xxx: Magnesium and silicon
- 7xxx: Zinc, magnesium, and copper
- 8xxx: other elements which are not covered by other series
There are also two principal classifications, namely casting alloys and wrought alloys, both of which are further subdivided into the categories heat-treatable and non-heat-treatable. Aluminium alloys containing alloying elements with limited solid solubility at room temperature and with a strong temperature dependence of solid solubility (for example Cu) can be strengthened by a suitable thermal treatment (precipitation hardening). The strength of heat treated commercial Al alloys exceeds 550 MPa.
Mechanical properties of aluminium alloys highly depend on their phase composition and microstructure. High strength can be achieved among others by introduction of a high volume fraction of fine, homogeneously distributed second phase particles and by a refinement of the grain size. In general, aluminium alloys are characterized by a relatively low density (2.7 g/cm3 as compared to 7.9 g/cm3 for steel), high electrical and thermal conductivities, and a resistance to corrosion in some common environments, including the ambient atmosphere. The chief limitation of aluminum is its low melting temperature (660°C), which restricts the maximum temperature at which it can be used. For general production the 5000 and 6000 series alloys provide adequate strength combined with good corrosion resistance, high toughness and ease of welding.
Strength of Aluminium Alloys
In mechanics of materials, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. Strength of materials basically considers the relationship between the external loads applied to a material and the resulting deformation or change in material dimensions. Strength of a material is its ability to withstand this applied load without failure or plastic deformation.
Ultimate Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength of 2024 aluminium alloy depends greatly on the temper of the material, but it is about 450 MPa.
Ultimate tensile strength of 6061 aluminium alloy depends greatly on the temper of the material, but for T6 temper it is about 290 MPa.
 The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension. Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to “tensile strength” or even to “the ultimate.” If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result. Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals). When a ductile material reaches its ultimate strength, it experiences necking where the cross-sectional area reduces locally. The stress-strain curve contains no higher stress than the ultimate strength. Even though deformations can continue to increase, the stress usually decreases after the ultimate strength has been achieved. It is an intensive property; therefore its value does not depend on the size of the test specimen. However, it is dependent on other factors, such as the preparation of the specimen, the presence or otherwise of surface defects, and the temperature of the test environment and material. Ultimate tensile strengths vary from 50 MPa for an aluminum to as high as 3000 MPa for very high-strength steels.
The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension. Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to “tensile strength” or even to “the ultimate.” If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result. Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals). When a ductile material reaches its ultimate strength, it experiences necking where the cross-sectional area reduces locally. The stress-strain curve contains no higher stress than the ultimate strength. Even though deformations can continue to increase, the stress usually decreases after the ultimate strength has been achieved. It is an intensive property; therefore its value does not depend on the size of the test specimen. However, it is dependent on other factors, such as the preparation of the specimen, the presence or otherwise of surface defects, and the temperature of the test environment and material. Ultimate tensile strengths vary from 50 MPa for an aluminum to as high as 3000 MPa for very high-strength steels.
Yield Strength
Yield strength of 2024 aluminium alloy depends greatly on the temper of the material, but it is about 300 MPa.
Yield strength of 6061 aluminium alloy depends greatly on the temper of the material, but for T6 temper it is about 240 MPa.
The yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior. Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins. Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible. Some steels and other materials exhibit a behaviour termed a yield point phenomenon. Yield strengths vary from 35 MPa for a low-strength aluminum to greater than 1400 MPa for very high-strength steels.
Young’s Modulus of Elasticity
Young’s modulus of elasticity of 2024 aluminium alloy is about 76 GPa.
Young’s modulus of elasticity of 6061 aluminium alloy is about 69 GPa.
The Young’s modulus of elasticity is the elastic modulus for tensile and compressive stress in the linear elasticity regime of a uniaxial deformation and is usually assessed by tensile tests. Up to a limiting stress, a body will be able to recover its dimensions on removal of the load. The applied stresses cause the atoms in a crystal to move from their equilibrium position. All the atoms are displaced the same amount and still maintain their relative geometry. When the stresses are removed, all the atoms return to their original positions and no permanent deformation occurs. According to the Hooke’s law, the stress is proportional to the strain (in the elastic region), and the slope is Young’s modulus. Young’s modulus is equal to the longitudinal stress divided by the strain.
We hope, this article, Strength of Aluminium Alloys, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.