Ionization Energy
Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom.
X + energy → X+ + e−
where X is any atom or molecule capable of being ionized, X+ is that atom or molecule with an electron removed (positive ion), and e− is the removed electron.
A nitrogen atom, for example, requires the following ionization energy to remove the outermost electron.
N + IE → N+ + e− IE = 14.5 eV
The ionization energy associated with removal of the first electron is most commonly used. The nth ionization energy refers to the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the species with a charge of (n-1).
1st ionization energy
X → X+ + e−
2nd ionization energy
X+ → X2+ + e−
3rd ionization energy
X2+ → X3+ + e−
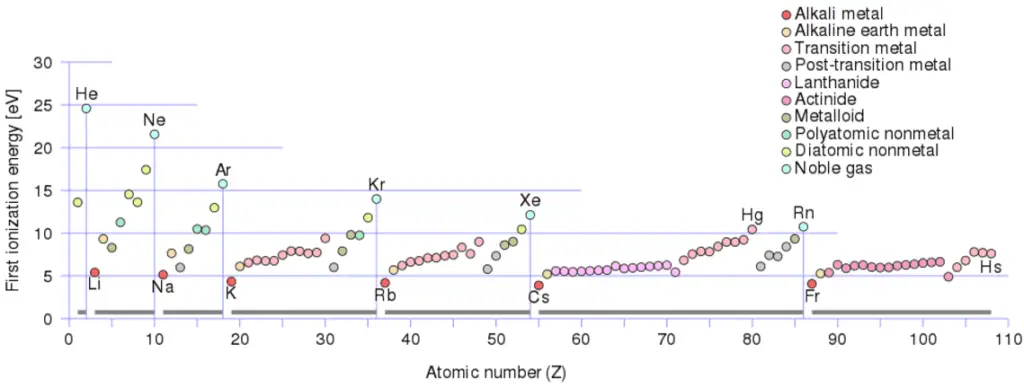
Ionization Energy for different Elements
There is an ionization energy for each successive electron removed. The electrons that circle the nucleus move in fairly well-defined orbits. Some of these electrons are more tightly bound in the atom than others. For example, only 7.38 eV is required to remove the outermost electron from a lead atom, while 88,000 eV is required to remove the innermost electron. Helps to understand reactivity of elements (especially metals, which lose electrons).
In general, the ionization energy increases moving up a group and moving left to right across a period. Moreover:
- Ionization energy is lowest for the alkali metals which have a single electron outside a closed shell.
- Ionization energy increases across a row on the periodic maximum for the noble gases which have closed shells
For example, sodium requires only 496 kJ/mol or 5.14 eV/atom to ionize it. On the other hand neon, the noble gas, immediately preceding it in the periodic table, requires 2081 kJ/mol or 21.56 eV/atom.
We hope, this article, Ionization Energy – Ionization Potential, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.