This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of europium and gadolinium, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Europium vs Gadolinium.
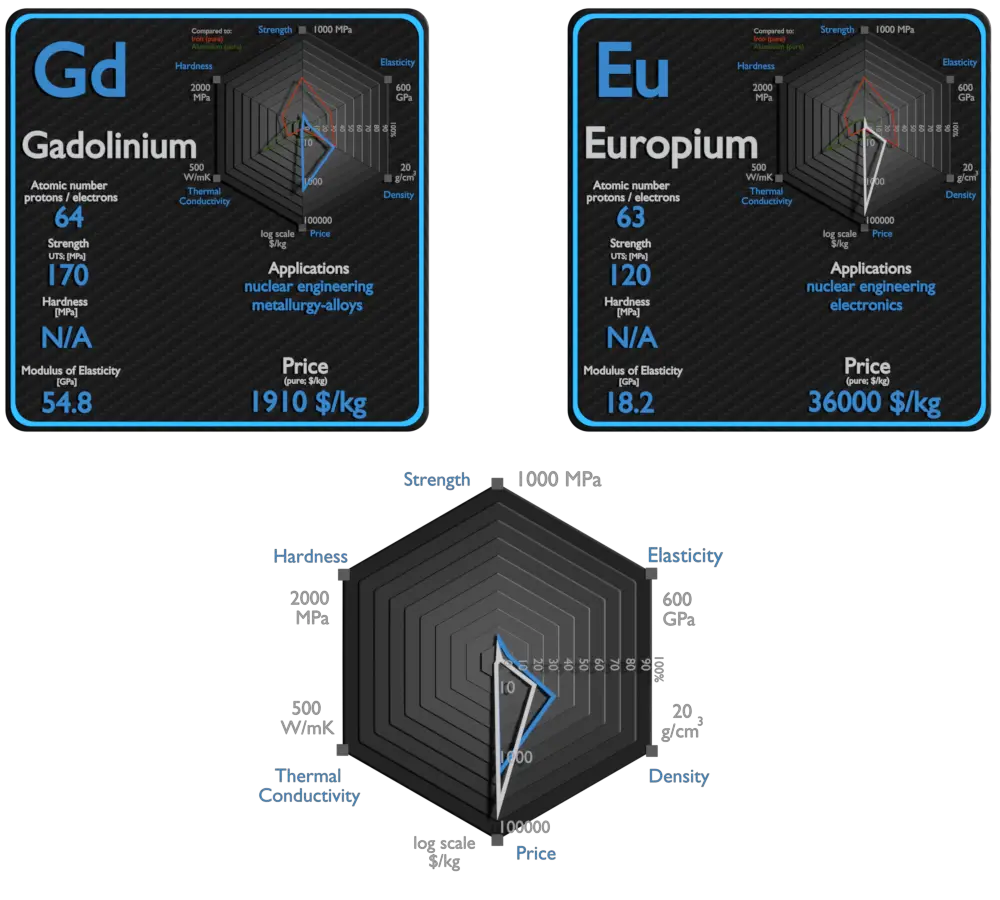
Europium and Gadolinium – About Elements


Source: www.luciteria.com
Europium and Gadolinium – Applications
Europium
Europium is used in the printing of euro banknotes. It glows red under UV light, and forgeries can be detected by the lack of this red glow. It is a dopant in some types of glass in lasers and other optoelectronic devices. Since the isotopes of europium act as good neutron absorbers, they are being studied for use in nuclear control applications, such as in burnable absorbers.
Gadolinium
Gadolinium possesses unusual metallurgical properties, to the extent that as little as 1% of gadolinium can significantly improve the workability and resistance to oxidation at high temperatures of iron, chromium, and related metals. Gadolinium as a metal or a salt absorbs neutrons and is, therefore, used sometimes for shielding in neutron radiography and in nuclear reactors. Gadolinium is widely used as a burnable absorber, which is commonly used in fresh fuel to compensate an excess of reactivity of reactor core. Among all known stable elements, gadolinium has the highest thermal neutron capture cross-section (49,000 barns). Gadolinium barium copper oxide (GdBCO) has been researched for its superconducting properties with applications in superconducting motors or generators – for example in a wind turbine.
Europium and Gadolinium – Comparison in Table
| Element | Europium | Gadolinium |
| Density | 5.244 g/cm3 | 7.901 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 120 MPa | 170 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 60 MPa | 160 MPa |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 18.2 GPa | 54.8 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | N/A | N/A |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A | N/A |
| Vickers Hardness | 170 MPa | 570 MPa |
| Melting Point | 822 °C | 1313 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1529 °C | 3000 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 14 W/mK | 11 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 35 µm/mK | 9.4 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.18 J/g K | 0.23 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 9.21 kJ/mol | 10.05 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 143.5 kJ/mol | 359.4 kJ/mol |




