This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of europium and tantalum, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Europium vs Tantalum.
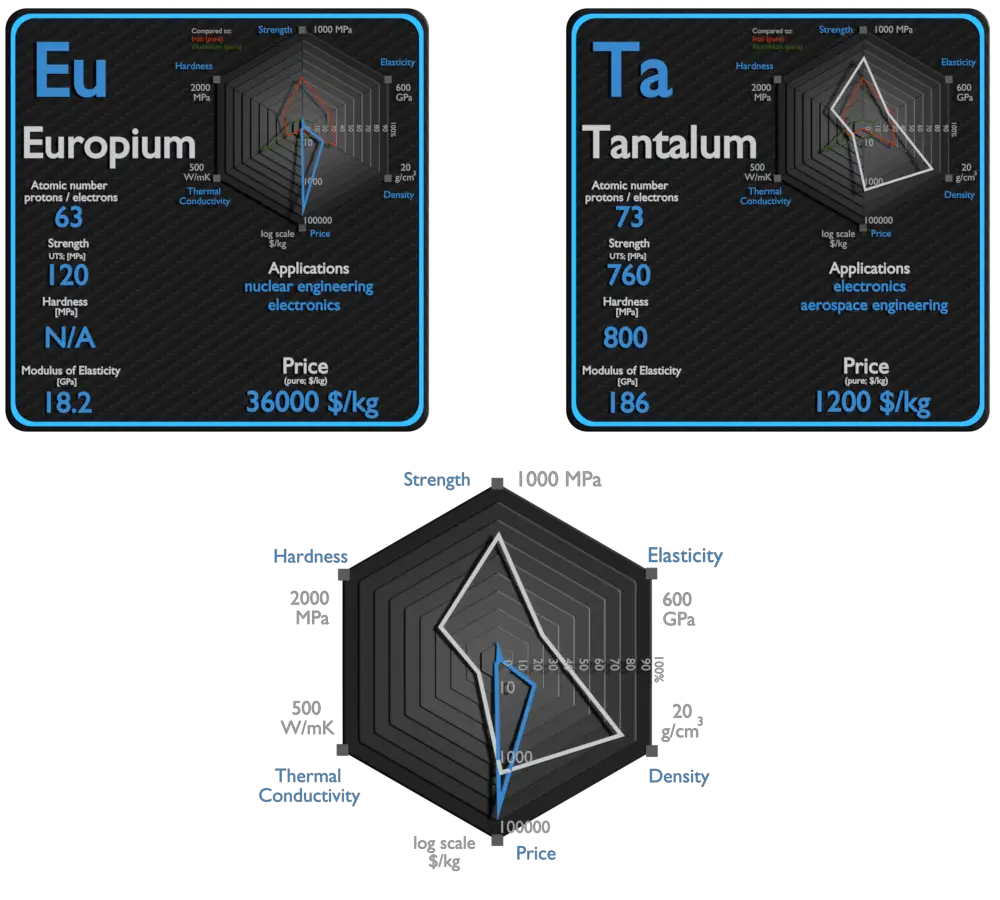
Europium and Tantalum – About Elements


Source: www.luciteria.com
Europium and Tantalum – Applications
Europium
Europium is used in the printing of euro banknotes. It glows red under UV light, and forgeries can be detected by the lack of this red glow. It is a dopant in some types of glass in lasers and other optoelectronic devices. Since the isotopes of europium act as good neutron absorbers, they are being studied for use in nuclear control applications, such as in burnable absorbers.
Tantalum
Tantalum consumption is dominated by capacitors for electronic equipment. Capacitors are electrical components that store energy electrostatically in an electric field, and are used in a wide variety of electric and electronic products. Major end uses for tantalum capacitors include portable telephones, pagers, personal computers, and automotive electronics. Alloyed with other metals, tantalum is also used in making carbide tools for metalworking equipment and in the production of superalloys for jet engine components. Compounds of tantalum such as tantalum pentoxide is used to make capacitors and glass with a high index of refraction for use in camera lenses.
Europium and Tantalum – Comparison in Table
| Element | Europium | Tantalum |
| Density | 5.244 g/cm3 | 16.65 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 120 MPa | 760 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 60 MPa | 705 MPa |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 18.2 GPa | 186 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | N/A | 6.5 |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A | 800 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness | 170 MPa | 870 MPa |
| Melting Point | 822 °C | 2996 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1529 °C | 5425 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 14 W/mK | 57 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 35 µm/mK | 6.3 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.18 J/g K | 0.14 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 9.21 kJ/mol | 31.6 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 143.5 kJ/mol | 743 kJ/mol |







