This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of europium and ytterbium, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Europium vs Ytterbium.
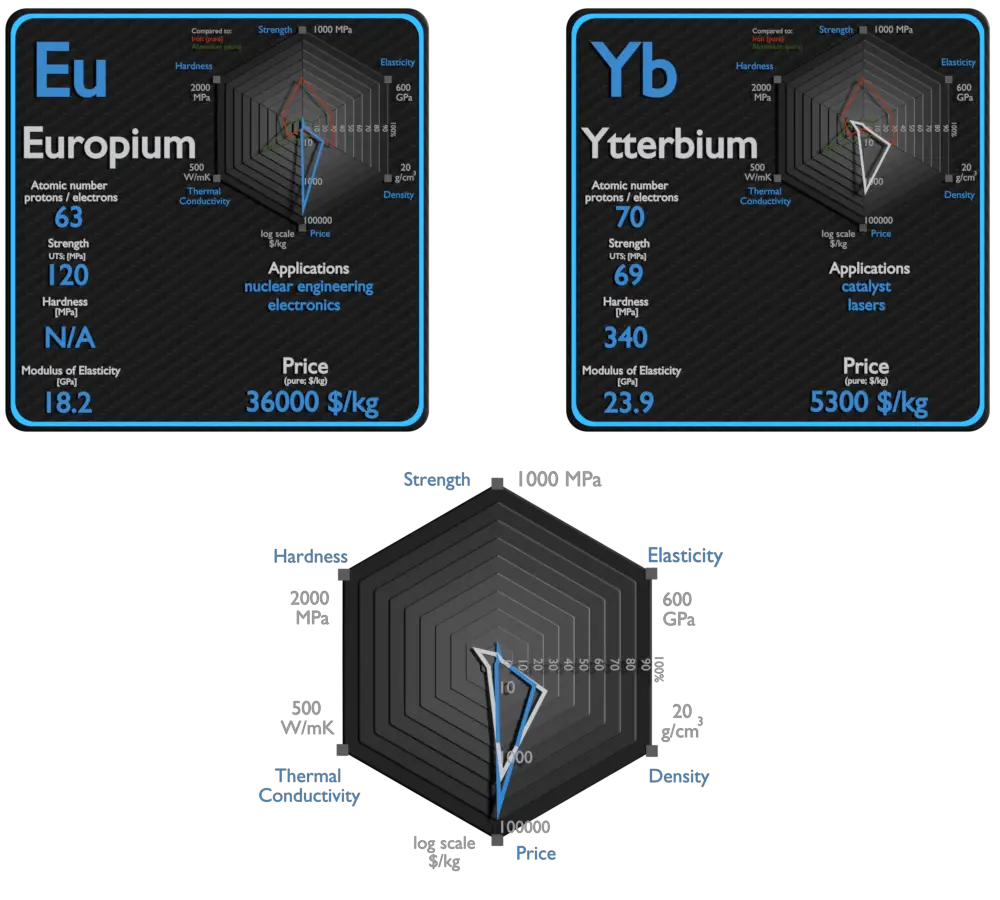
Europium and Ytterbium – About Elements


Source: www.luciteria.com
Europium and Ytterbium – Applications
Europium
Europium is used in the printing of euro banknotes. It glows red under UV light, and forgeries can be detected by the lack of this red glow. It is a dopant in some types of glass in lasers and other optoelectronic devices. Since the isotopes of europium act as good neutron absorbers, they are being studied for use in nuclear control applications, such as in burnable absorbers.
Ytterbium
Ytterbium is beginning to find a variety of uses, such as in memory devices and tuneable lasers. It can also be used as an industrial catalyst and is increasingly being used to replace other catalysts considered to be too toxic and polluting. A small amount of ytterbium is used to add strength to specific steel types. Ytterbium can also be used as a dopant to help improve the grain refinement, strength, and other mechanical properties of stainless steel.
Europium and Ytterbium – Comparison in Table
| Element | Europium | Ytterbium |
| Density | 5.244 g/cm3 | 6.57 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 120 MPa | 69 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 60 MPa | 66 MPa |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 18.2 GPa | 23.9 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | N/A | N/A |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A | 340 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness | 170 MPa | 210 MPa |
| Melting Point | 822 °C | 819 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1529 °C | 1196 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 14 W/mK | 39 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 35 µm/mK | 26.3 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.18 J/g K | 0.15 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 9.21 kJ/mol | 7.66 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 143.5 kJ/mol | 128.9 kJ/mol |