This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of neon and xenon, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Neon vs Xenon.
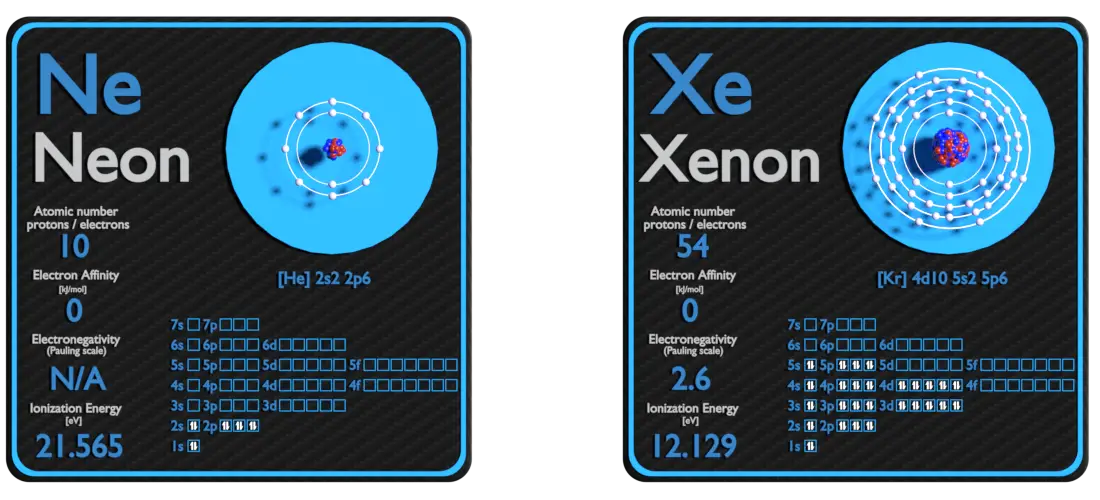
Neon and Xenon – About Elements


Source: www.luciteria.com
Neon and Xenon – Applications
Neon
Neon is often used in signs and produces an unmistakable bright reddish-orange light. Although tube lights with other colors are often called “neon”, they use different noble gases or varied colors of fluorescent lighting. Neon is also used to make high-voltage indicators and switching gear, lightning arresters, diving equipment and lasers. Liquid neon is an important cryogenic refrigerant. It has over 40 times more refrigerating capacity per unit volume than liquid helium, and more than 3 times that of liquid hydrogen.
Xenon
Xenon is useful in the following applications. The white flash of light produced by xenon makes it suitable for usage in strobe lights and to power ruby lasers. Xenon is used in light-emitting devices called xenon flash lamps, used in photographic flashes and stroboscopic lamps.
Neon and Xenon – Comparison in Table
| Element | Neon | Xenon |
| Density | 0.0009 g/cm3 | 0.0059 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | N/A | N/A |
| Yield Strength | N/A | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | N/A | N/A |
| Mohs Scale | N/A | N/A |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A | N/A |
| Vickers Hardness | N/A | N/A |
| Melting Point | -248 °C | -111.8 °C |
| Boiling Point | -248.7 °C | -107.1 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.0493 W/mK | 0.00565 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | N/A | N/A |
| Specific Heat | 0.904 J/g K | 0.158 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 0.3317 kJ/mol | 2.297 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 1.7326 kJ/mol | 12.636 kJ/mol |





