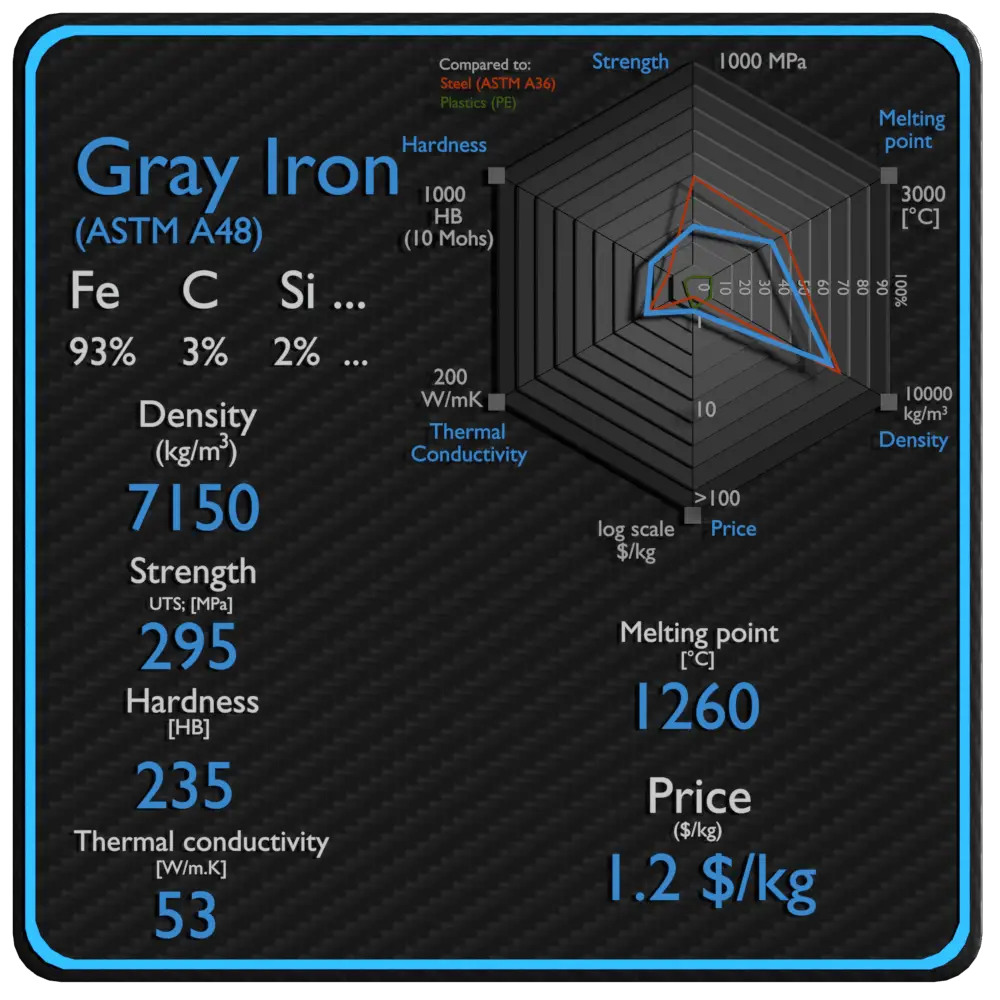
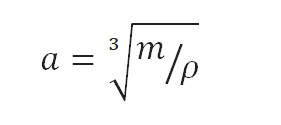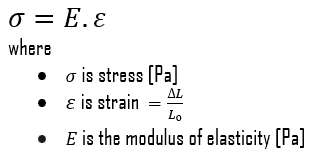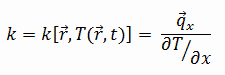About Gray Iron
Gray cast iron is the oldest and most common type of iron in existence and probably what most people think of when they hear the term “cast iron”. The carbon and silicon contents of gray cast irons vary between 2.5 and 4.0 wt% and 1.0 and 3.0 wt%, respectively.

Gray cast iron is characterised by its graphitic microstructure, which causes fractures of the material to have a gray appearance. This is due to the presence of graphite in its composition. In gray cast iron the graphite forms as flakes, taking on a three dimensional geometry.
Gray cast iron has less tensile strength and shock resistance than steel, but its compressive strength is comparable to low- and medium-carbon steel. Gray cast iron has good thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity, therefore it is often used in cookware and brake rotors.
Summary
| Name | Gray Iron |
| Phase at STP | solid |
| Density | 7150 kg/m3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 395 MPa |
| Yield Strength | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 124 GPa |
| Brinell Hardness | 235 BHN |
| Melting Point | 1260 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 53 W/mK |
| Heat Capacity | 460 J/g K |
| Price | 1.2 $/kg |
Density of Gray Iron
Typical densities of various substances are at atmospheric pressure. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: ρ = m/V
In words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance. The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3). The Standard English unit is pounds mass per cubic foot (lbm/ft3).
Density of Gray Iron is 7150 kg/m3.
Example: Density
Calculate the height of a cube made of Gray Iron, which weighs one metric ton.
Solution:
Density is defined as the mass per unit volume. It is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: ρ = m/V
As the volume of a cube is the third power of its sides (V = a3), the height of this cube can be calculated:
The height of this cube is then a = 0.519 m.
Density of Materials
Mechanical Properties of Gray Iron
Materials are frequently chosen for various applications because they have desirable combinations of mechanical characteristics. For structural applications, material properties are crucial and engineers must take them into account.
Strength of Gray Iron
In mechanics of materials, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. Strength of materials basically considers the relationship between the external loads applied to a material and the resulting deformation or change in material dimensions. Strength of a material is its ability to withstand this applied load without failure or plastic deformation.
Ultimate Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength of Gray Iron (ASTM A48 Class 40) is 295 MPa.
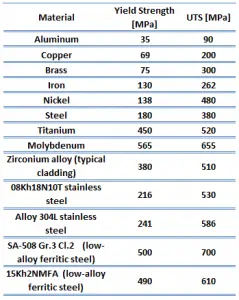 The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension. Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to “tensile strength” or even to “the ultimate.” If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result. Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals). When a ductile material reaches its ultimate strength, it experiences necking where the cross-sectional area reduces locally. The stress-strain curve contains no higher stress than the ultimate strength. Even though deformations can continue to increase, the stress usually decreases after the ultimate strength has been achieved. It is an intensive property; therefore its value does not depend on the size of the test specimen. However, it is dependent on other factors, such as the preparation of the specimen, the presence or otherwise of surface defects, and the temperature of the test environment and material. Ultimate tensile strengths vary from 50 MPa for an aluminum to as high as 3000 MPa for very high-strength steels.
The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension. Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to “tensile strength” or even to “the ultimate.” If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result. Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals). When a ductile material reaches its ultimate strength, it experiences necking where the cross-sectional area reduces locally. The stress-strain curve contains no higher stress than the ultimate strength. Even though deformations can continue to increase, the stress usually decreases after the ultimate strength has been achieved. It is an intensive property; therefore its value does not depend on the size of the test specimen. However, it is dependent on other factors, such as the preparation of the specimen, the presence or otherwise of surface defects, and the temperature of the test environment and material. Ultimate tensile strengths vary from 50 MPa for an aluminum to as high as 3000 MPa for very high-strength steels.
Young’s Modulus of Elasticity
Young’s modulus of elasticity of Gray Iron (ASTM A48 Class 40) is 124 GPa.
The Young’s modulus of elasticity is the elastic modulus for tensile and compressive stress in the linear elasticity regime of a uniaxial deformation and is usually assessed by tensile tests. Up to a limiting stress, a body will be able to recover its dimensions on removal of the load. The applied stresses cause the atoms in a crystal to move from their equilibrium position. All the atoms are displaced the same amount and still maintain their relative geometry. When the stresses are removed, all the atoms return to their original positions and no permanent deformation occurs. According to the Hooke’s law, the stress is proportional to the strain (in the elastic region), and the slope is Young’s modulus. Young’s modulus is equal to the longitudinal stress divided by the strain.
Hardness of Gray Cast Iron – ASTM A48 Class 40
Brinell hardness of Gray Iron (ASTM A48 Class 40) is approximately 235 MPa.
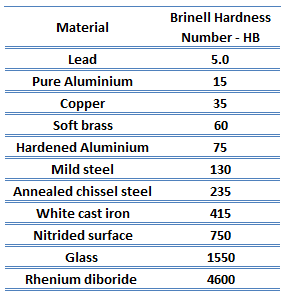 In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation (localized plastic deformation) and scratching. Hardness is probably the most poorly defined material property because it may indicate resistance to scratching, resistance to abrasion, resistance to indentation or even resistance to shaping or localized plastic deformation. Hardness is important from an engineering standpoint because resistance to wear by either friction or erosion by steam, oil, and water generally increases with hardness.
In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation (localized plastic deformation) and scratching. Hardness is probably the most poorly defined material property because it may indicate resistance to scratching, resistance to abrasion, resistance to indentation or even resistance to shaping or localized plastic deformation. Hardness is important from an engineering standpoint because resistance to wear by either friction or erosion by steam, oil, and water generally increases with hardness.
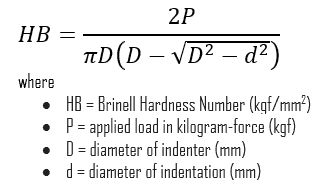
Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter hardened steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29.42 kN; 6,614 lbf) force. The load is maintained constant for a specified time (between 10 and 30 s). For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball.
The test provides numerical results to quantify the hardness of a material, which is expressed by the Brinell hardness number – HB. The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide). In former standards HB or HBS were used to refer to measurements made with steel indenters.
The Brinell hardness number (HB) is the load divided by the surface area of the indentation. The diameter of the impression is measured with a microscope with a superimposed scale. The Brinell hardness number is computed from the equation:
There are a variety of test methods in common use (e.g. Brinell, Knoop, Vickers and Rockwell). There are tables that are available correlating the hardness numbers from the different test methods where correlation is applicable. In all scales, a high hardness number represents a hard metal.
Example: Strength
Assume a plastic rod, which is made of Gray Iron. This plastic rod has a cross-sectional area of 1 cm2. Calculate the tensile force needed to achieve the ultimate tensile strength for this material, which is: UTS = 295 MPa.
Solution:
Stress (σ) can be equated to the load per unit area or the force (F) applied per cross-sectional area (A) perpendicular to the force as:
therefore, the tensile force needed to achieve the ultimate tensile strength is:
F = UTS x A = 295 x 106 x 0.0001 = 29 500 N
Thermal Properties of Gray Iron
Thermal properties of materials refer to the response of materials to changes in their thermodynamics/thermodynamic-properties/what-is-temperature-physics/”>temperature and to the application of heat. As a solid absorbs thermodynamics/what-is-energy-physics/”>energy in the form of heat, its temperature rises and its dimensions increase. But different materials react to the application of heat differently.
Heat capacity, thermal expansion, and thermal conductivity are properties that are often critical in the practical use of solids.
Melting Point of Gray Gray Iron
Melting point of Gray Iron is around 1260°C.
In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium.
Thermal Conductivity of Gray Iron
The thermal conductivity of Gray Iron is 53 W/(m.K).
The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.K. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Note that Fourier’s law applies for all matter, regardless of its state (solid, liquid, or gas), therefore, it is also defined for liquids and gases.
The thermal conductivity of most liquids and solids varies with temperature. For vapors, it also depends upon pressure. In general:
Most materials are very nearly homogeneous, therefore we can usually write k = k (T). Similar definitions are associated with thermal conductivities in the y- and z-directions (ky, kz), but for an isotropic material the thermal conductivity is independent of the direction of transfer, kx = ky = kz = k.
Example: Heat transfer calculation
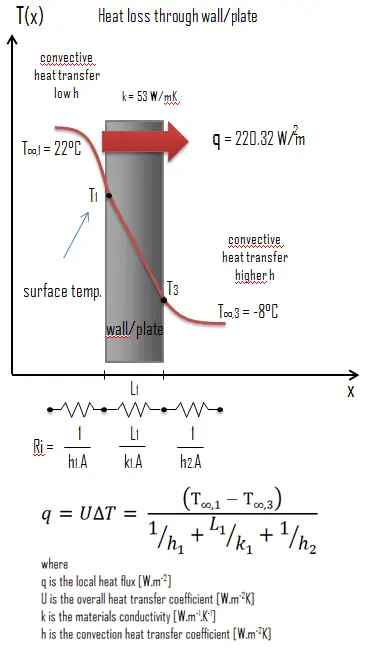 Thermal conductivity is defined as the amount of heat (in watts) transferred through a square area of material of given thickness (in metres) due to a difference in temperature. The lower the thermal conductivity of the material the greater the material’s ability to resist heat transfer.
Thermal conductivity is defined as the amount of heat (in watts) transferred through a square area of material of given thickness (in metres) due to a difference in temperature. The lower the thermal conductivity of the material the greater the material’s ability to resist heat transfer.
Calculate the rate of heat flux through a wall 3 m x 10 m in area (A = 30 m2). The wall is 15 cm thick (L1) and it is made of Gray Iron with the thermal conductivity of k1 = 53 W/m.K (poor thermal insulator). Assume that, the indoor and the outdoor temperatures are 22°C and -8°C, and the convection heat transfer coefficients on the inner and the outer sides are h1 = 10 W/m2K and h2 = 30 W/m2K, respectively. Note that, these convection coefficients strongly depend especially on ambient and interior conditions (wind, humidity, etc.).
Calculate the heat flux (heat loss) through this wall.
Solution:
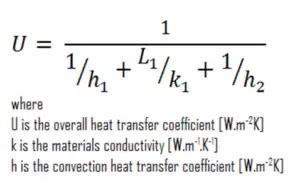
As was written, many of the heat transfer processes involve composite systems and even involve a combination of both conduction and convection. With these composite systems, it is often convenient to work with an overall heat transfer coefficient, known as a U-factor. The U-factor is defined by an expression analogous to Newton’s law of cooling:
The overall heat transfer coefficient is related to the total thermal resistance and depends on the geometry of the problem.
Assuming one-dimensional heat transfer through the plane wall and disregarding radiation, the overall heat transfer coefficient can be calculated as:
The overall heat transfer coefficient is then: U = 1 / (1/10 + 0.15/53 + 1/30) = 7.34 W/m2K
The heat flux can be then calculated simply as: q = 7.34 [W/m2K] x 30 [K] = 220.32 W/m2
The total heat loss through this wall will be: qloss = q . A = 220.32 [W/m2] x 30 [m2] = 6609.7 W
We hope, this article, Gray Iron – Gray Cast Iron, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about materials and their properties.