This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of sodium and sulfur, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Sodium vs Sulfur.
Sodium and Sulfur – About Elements

Source: www.luciteria.com
Sodium and Sulfur – Applications
Sodium
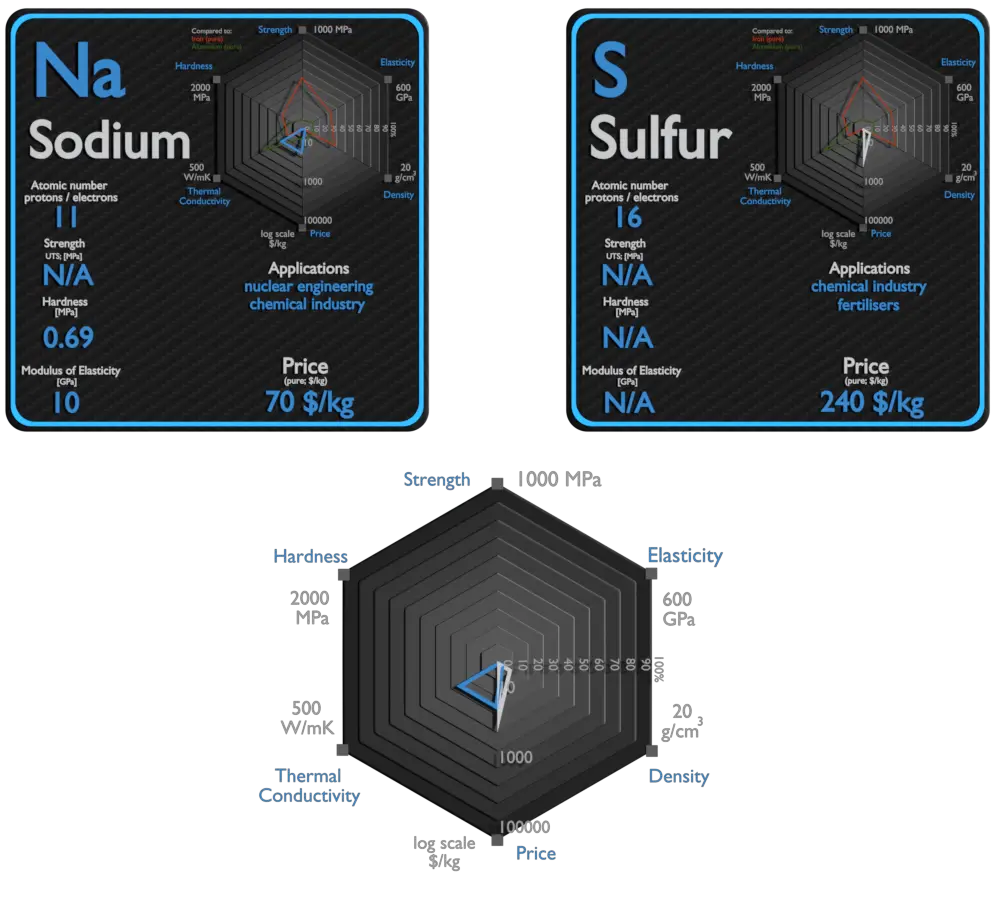
Metallic sodium is used mainly for the production of sodium borohydride, sodium azide, indigo, and triphenylphosphine. A once-common use was the making of tetraethyllead and titanium metal; because of the move away from TEL and new titanium production methods. An electric current and sodium vapor combine to form a yellowish glow. This principle is used for the making of sodium vapor lamps. Sodium is occasionally used as a heat exchange medium in nuclear power plants. Liquid sodium is sealed into pipes surrounding the reactor core. Generated heat is absorbed by sodium and forced through the pipes in a heat exchanger which can be used to generate electricity.
Sulfur
The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of sulfuric acid for sulfate and phosphate fertilizers, and other chemical processes. Sulfur is increasingly used as a component of fertilizers. The most important form of sulfur for fertilizer is the mineral calcium sulfate. The element sulfur is used in matches, insecticides, and fungicides. Many sulfur compounds are odoriferous, and the smells of odorized natural gas, skunk scent, grapefruit, and garlic are due to organosulfur compounds.
Sodium and Sulfur – Comparison in Table
| Element | Sodium | Sulfur |
| Density | 0.968 g/cm3 | 1.96 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | N/A | N/A |
| Yield Strength | N/A | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 10 GPa | N/A |
| Mohs Scale | 0.4 | 2 |
| Brinell Hardness | 0.69 MPa | N/A |
| Vickers Hardness | N/A | N/A |
| Melting Point | 97.8 °C | 112.8 °C |
| Boiling Point | 883 °C | 444.7 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 141 W/mK | 0.269 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 71 µm/mK | N/A |
| Specific Heat | 1.23 J/g K | 0.71 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 2.598 kJ/mol | 1.7175 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 96.96 kJ/mol | 45 kJ/mol |