This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of sulfur and potassium, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Sulfur vs Potassium.
Sulfur and Potassium – About Elements

Source: www.luciteria.com
Sulfur and Potassium – Applications
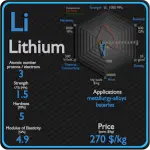
Sulfur
The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of sulfuric acid for sulfate and phosphate fertilizers, and other chemical processes. Sulfur is increasingly used as a component of fertilizers. The most important form of sulfur for fertilizer is the mineral calcium sulfate. The element sulfur is used in matches, insecticides, and fungicides. Many sulfur compounds are odoriferous, and the smells of odorized natural gas, skunk scent, grapefruit, and garlic are due to organosulfur compounds.
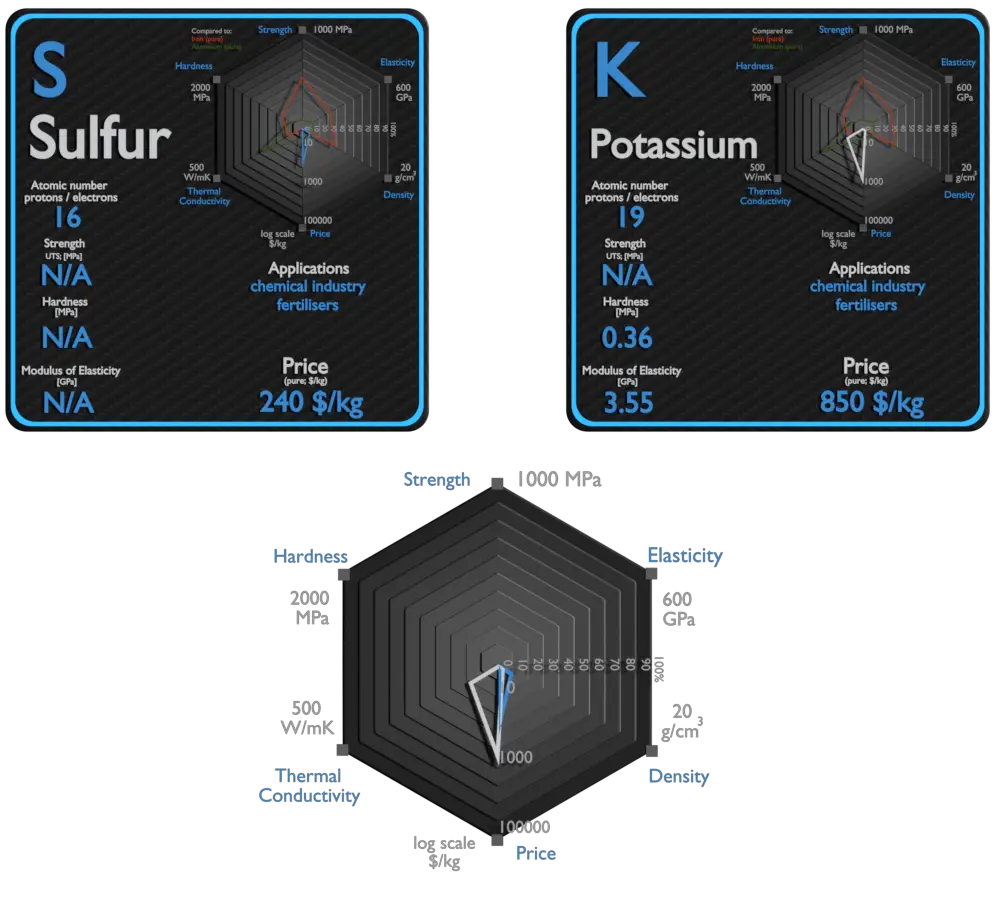
Potassium
Potassium (K) is an essential nutrient for plant growth. It’s classified as a macronutrient because plants take up large quantities of K during their life cycle. Agricultural fertilizers consume 95% of global potassium chemical production, and about 90% of this potassium is supplied as KCl. Due to its high degree of reactivity, pure potassium is rarely used in its elemental /metallic form. It is used as a powerful reducing agent in organic chemistry. Potassium/Sodium alloys are It used as a heat exchange medium . The heat in the potassium warms water and makes it hot enough to boil. Then water is changed into steam, which is used to work devices that generate electricity.
Sulfur and Potassium – Comparison in Table
| Element | Sulfur | Potassium |
| Density | 1.823 g/cm3 | 0.856 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | N/A | N/A |
| Yield Strength | N/A | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | N/A | 3.53 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A | 0.36 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness | N/A | N/A |
| Melting Point | 44.1 °C | 63.25 °C |
| Boiling Point | 280 °C | 760 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.235 W/mK | 102.4 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | N/A | 83 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.77 J/g K | 0.75 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 0.657 kJ/mol | 2.334 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 51.9 kJ/mol | 79.87 kJ/mol |