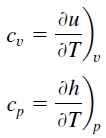About Thorium
Thorium metal is silvery and tarnishes black when exposed to air, forming the dioxide. Thorium is moderately hard, malleable, and has a high melting point. Thorium is a naturally-occurring element and it is estimated to be about three times more abundant than uranium. Thorium is commonly found in monazite sands (rare earth metals containing phosphate mineral).
Thorium – Specific Heat, Latent Heat of Fusion, Latent Heat of Vaporization
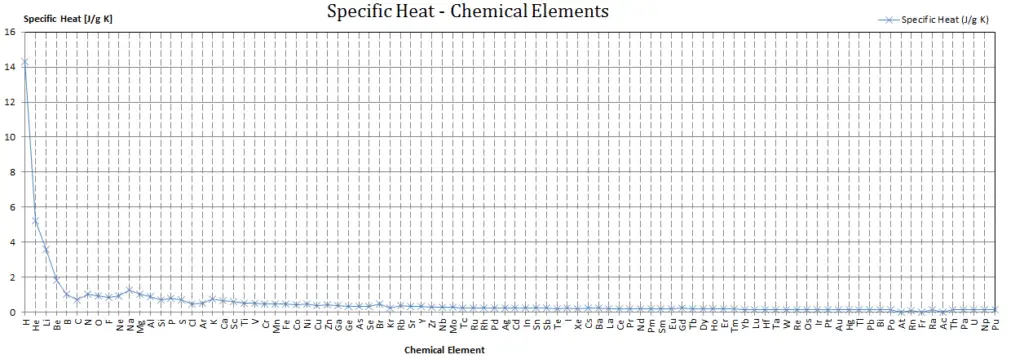
Specific heat of Thorium is 0.12 J/g K.
Heat capacity is an extensive property of matter, meaning it is proportional to the size of the system. Heat capacity C has the unit of energy per degree or energy per kelvin. When expressing the same phenomenon as an intensive property, the heat capacity is divided by the amount of substance, mass, or volume, thus the quantity is independent of the size or extent of the sample.
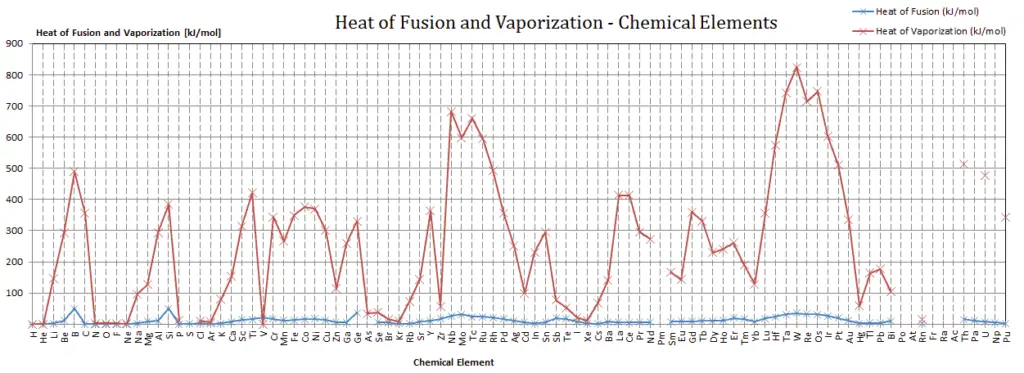
Latent Heat of Fusion of Thorium is 13.8 kJ/mol.
Latent Heat of Vaporization of Thorium is 514.4 kJ/mol.
Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a change in phase. This energy breaks down the intermolecular attractive forces, and also must provide the energy necessary to expand the gas (the pΔV work). When latent heat is added, no temperature change occurs. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place.
See also: Mechanical Properties of Thorium
Summary
| Element | Thorium |
| Specific Heat | 0.12 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 13.8 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 514.4 kJ/mol |
| Density | 11.724 g/cm3 |
Source: www.luciteria.com