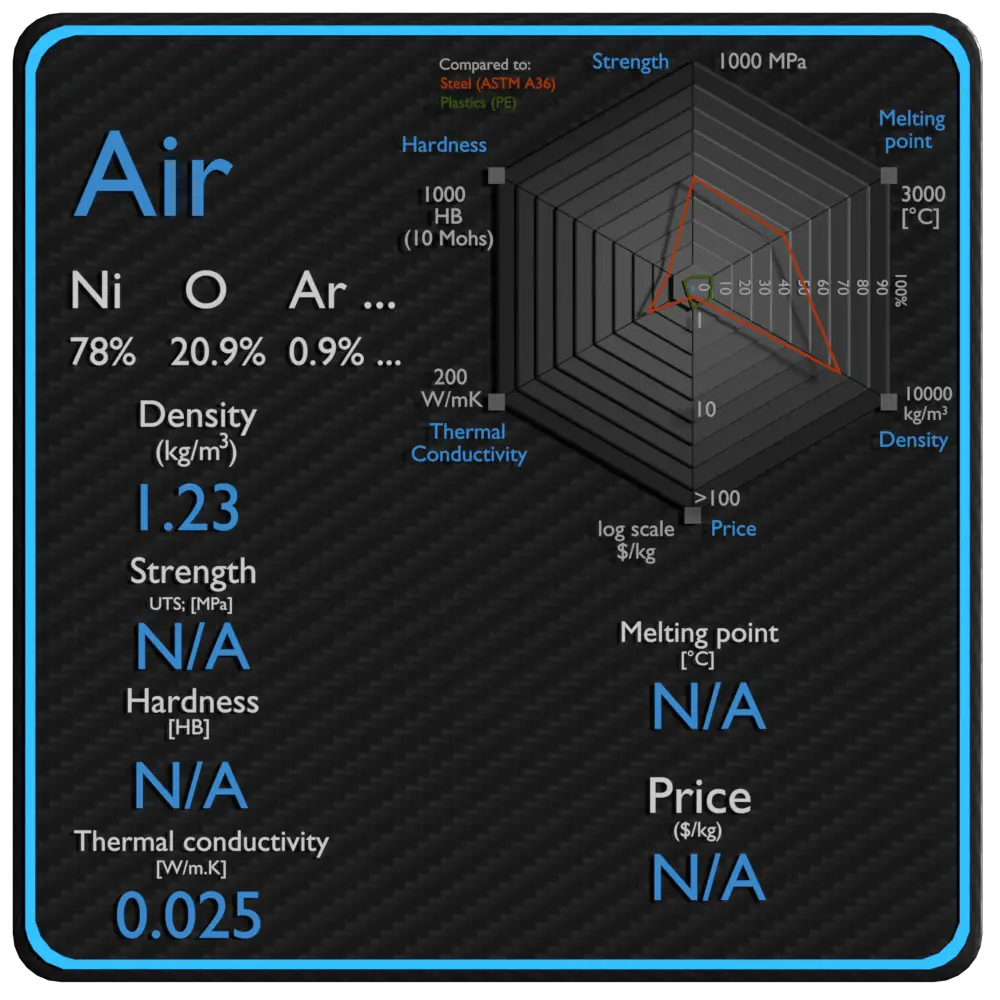
About Air
Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and other trace elements. The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, commonly known as air, retained by Earth’s gravity, surrounding the planet Earth and forming its planetary atmosphere.
Summary
| Name | Air |
| Phase at STP | gaseous |
| Density | 1.23 kg/m3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | N/A |
| Yield Strength | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | N/A |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A |
| Melting Point | N/A |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.025 W/mK |
| Heat Capacity | 1006 J/g K |
| Price | N/A |
Density of Air
Typical densities of various substances are at atmospheric pressure. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: ρ = m/V
In words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance. The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3). The Standard English unit is pounds mass per cubic foot (lbm/ft3).
Density of Air is 1.23 kg/m3.
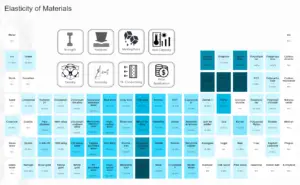
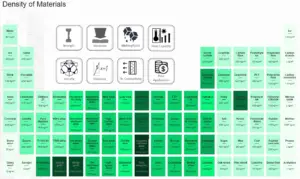
Density of Materials
Thermal Properties of Air
Air – Melting Point and Boiling Point
Melting point of Air is N/A.
Boiling point of Air is N/A.
Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure.
Air – Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity of Air is 0.025 W/(m·K).
The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.K. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Note that Fourier’s law applies for all matter, regardless of its state (solid, liquid, or gas), therefore, it is also defined for liquids and gases.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Air
Linear thermal expansion coefficient of Air is N/A.
Thermal expansion is generally the tendency of matter to change its dimensions in response to a change in temperature. It is usually expressed as a fractional change in length or volume per unit temperature change.
Air – Specific Heat, Latent Heat of Fusion, Latent Heat of Vaporization
Specific heat of Air is 1006 J/g K.
Heat capacity is an extensive property of matter, meaning it is proportional to the size of the system. Heat capacity C has the unit of energy per degree or energy per kelvin. When expressing the same phenomenon as an intensive property, the heat capacity is divided by the amount of substance, mass, or volume, thus the quantity is independent of the size or extent of the sample.
Latent Heat of Fusion of Air is N/A.
Latent Heat of Vaporization of Air is N/A.
Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a change in phase. This energy breaks down the intermolecular attractive forces, and also must provide the energy necessary to expand the gas (the pΔV work). When latent heat is added, no temperature change occurs. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place.