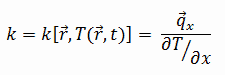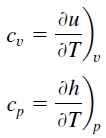About Quartz
Quartz is very abundant mineral of many varieties that consists primarily of silica, or silicon dioxide (SiO2). There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are semi-precious gemstones. Amethyst is a form of quartz that ranges from a bright vivid violet to dark or dull lavender shade. Citrine is a variety of quartz whose color ranges from a pale yellow to brown due to ferric impurities. Quartz is the mineral defining the value of 7 on the Mohs scale of hardness, a qualitative scratch method for determining the hardness of a material to abrasion.
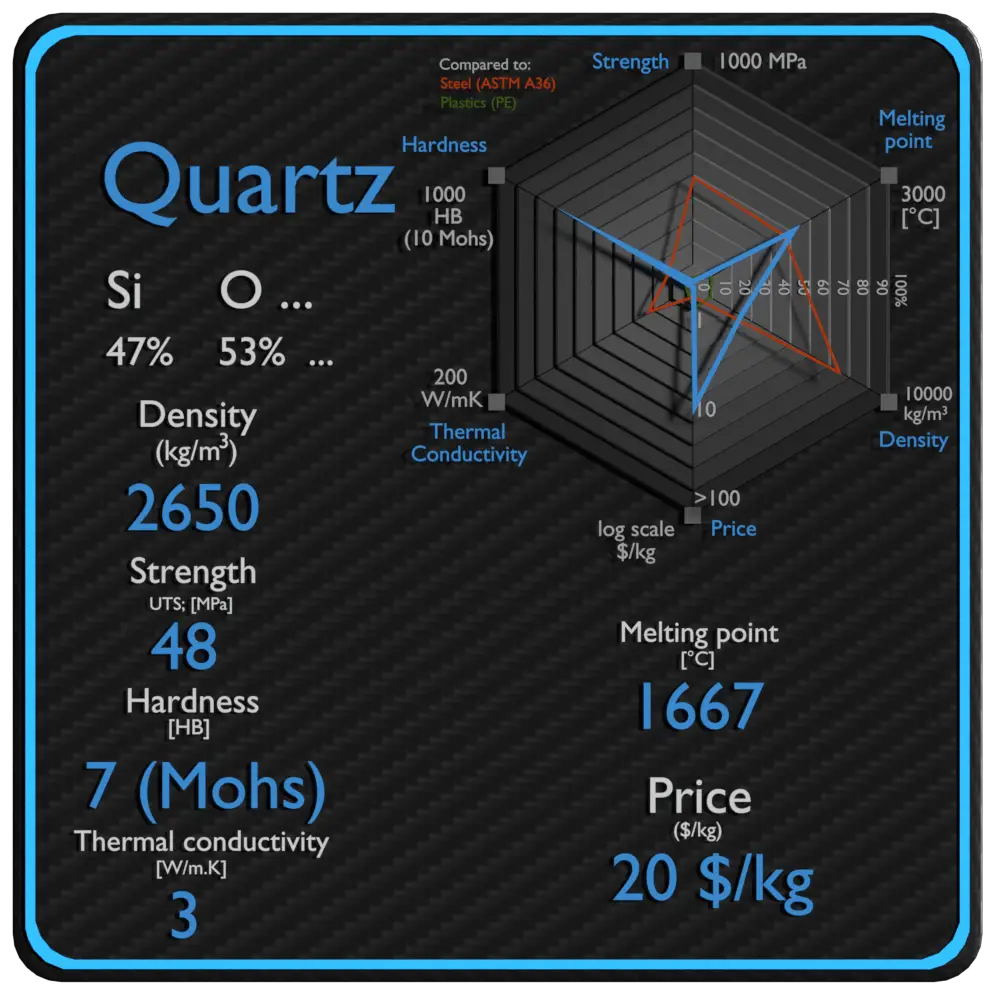
Summary
| Name | Quartz |
| Phase at STP | solid |
| Density | 2650 kg/m3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 48 MPa |
| Yield Strength | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 37 GPa |
| Brinell Hardness | 7 Mohs |
| Melting Point | 1667 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 3 W/mK |
| Heat Capacity | 741 J/g K |
| Price | 20 $/kg |
Composition of Quartz
Quartz is a chemical compound consisting of one part silicon and two parts oxygen. It is silicon dioxide (SiO2). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2.
Applications of Quartz

Quartz has great economic importance. Many varieties are gemstones, including amethyst, citrine, smoky quartz, and rose quartz. It has electrical properties (e.g. its piezoelectricity) and heat resistance that make it valuable in electronic products. Sandstone, composed mainly of quartz, is an important building stone. Large amounts of quartz sand (also known as silica sand) are used in the manufacture of glass and ceramics and for foundry molds in metal casting.Crushed quartz is used as an abrasive in sandpaper, silica sand is employed in sandblasting.
Mechanical Properties of Quartz
Strength of Quartz
In mechanics of materials, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. Strength of materials basically considers the relationship between the external loads applied to a material and the resulting deformation or change in material dimensions. In designing structures and machines, it is important to consider these factors, in order that the material selected will have adequate strength to resist applied loads or forces and retain its original shape.
Strength of a material is its ability to withstand this applied load without failure or plastic deformation. For tensile stress, the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to elongate is known as ultimate tensile strength (UTS). Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins. In case of tensional stress of a uniform bar (stress-strain curve), the Hooke’s law describes behaviour of a bar in the elastic region. The Young’s modulus of elasticity is the elastic modulus for tensile and compressive stress in the linear elasticity regime of a uniaxial deformation and is usually assessed by tensile tests.
See also: Strength of Materials
Ultimate Tensile Strength of Quartz
Ultimate tensile strength of Quartz is 48 MPa.
Yield Strength of Quartz
Yield strength of Quartz is N/A.
Modulus of Elasticity of Quartz
The Young’s modulus of elasticity of Quartz is 37 GPa.
Hardness of Quartz
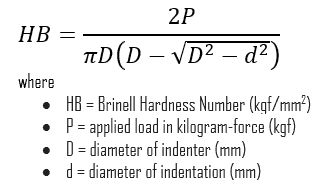
In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation (localized plastic deformation) and scratching. Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested.
The Brinell hardness number (HB) is the load divided by the surface area of the indentation. The diameter of the impression is measured with a microscope with a superimposed scale. The Brinell hardness number is computed from the equation:
Hardness of Quartz is approximately 7 Mohs.
See also: Hardness of Materials
Thermal Properties of Quartz
Quartz – Melting Point
Melting point of Quartz is 1667 °C.
Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. For various chemical compounds and alloys, it is difficult to define the melting point, since they are usually a mixture of various chemical elements.
Quartz – Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity of Quartz is 3 W/(m·K).
The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.K. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Note that Fourier’s law applies for all matter, regardless of its state (solid, liquid, or gas), therefore, it is also defined for liquids and gases.
The thermal conductivity of most liquids and solids varies with temperature. For vapors, it also depends upon pressure. In general:
Most materials are very nearly homogeneous, therefore we can usually write k = k (T). Similar definitions are associated with thermal conductivities in the y- and z-directions (ky, kz), but for an isotropic material the thermal conductivity is independent of the direction of transfer, kx = ky = kz = k.
Quartz – Specific Heat
Specific heat of Quartz is 741 J/g K.
Specific heat, or specific heat capacity, is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics. The intensive properties cv and cp are defined for pure, simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of the internal energy u(T, v) and enthalpy h(T, p), respectively:
where the subscripts v and p denote the variables held fixed during differentiation. The properties cv and cp are referred to as specific heats (or heat capacities) because under certain special conditions they relate the temperature change of a system to the amount of energy added by heat transfer. Their SI units are J/kg K or J/mol K.
Properties and prices of other materials
material-table-in-8k-resolution