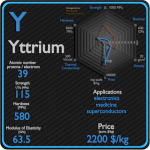
This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of yttrium and ytterbium, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Yttrium vsYtterbium.
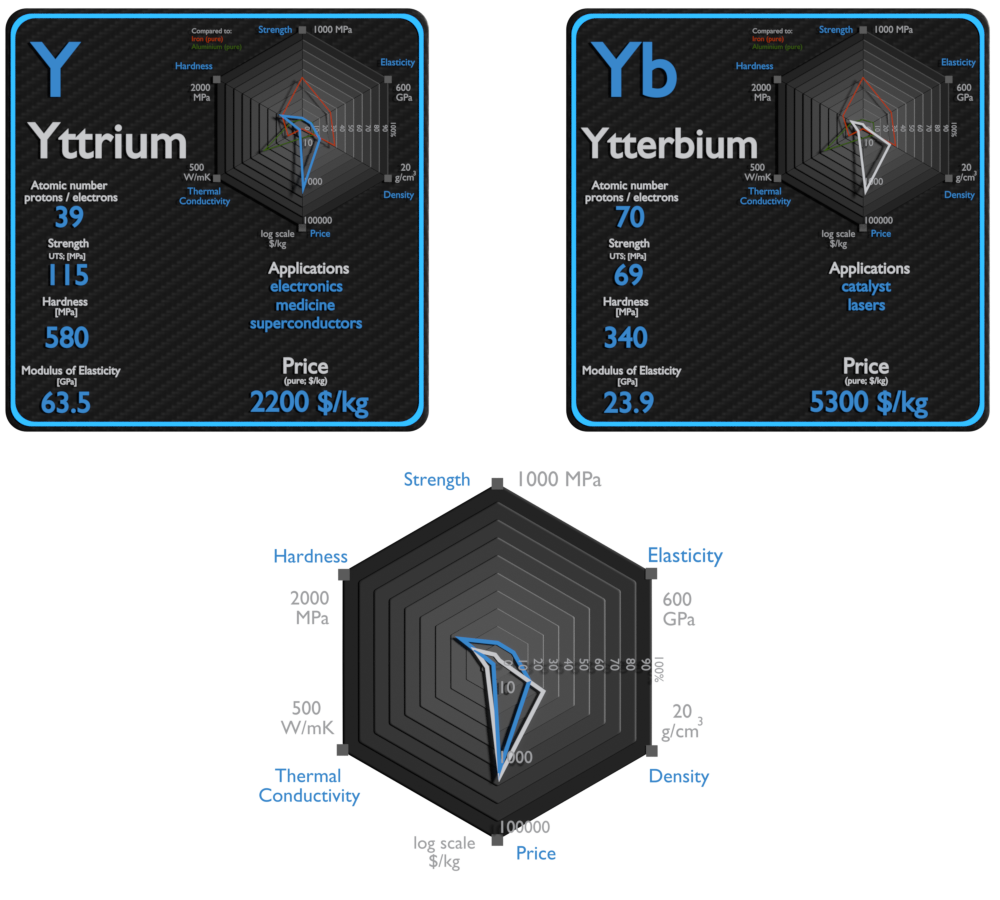
Yttrium and Ytterbium – About Elements


Source: www.luciteria.com
Yttrium and Ytterbium – Applications
Yttrium
The most important uses of yttrium are LEDs and phosphors, particularly the red phosphors in television set cathode ray tube displays. Yttrium is also used in the production of electrodes, electrolytes, electronic filters, lasers, superconductors, various medical applications, and tracing various materials to enhance their properties. Small amounts of yttrium (0.1 to 0.2%) have been used to reduce the grain sizes of chromium, molybdenum, titanium, and zirconium. Yttrium is used to increase the strength of aluminium and magnesium alloys.
Ytterbium
Ytterbium is beginning to find a variety of uses, such as in memory devices and tuneable lasers. It can also be used as an industrial catalyst and is increasingly being used to replace other catalysts considered to be too toxic and polluting. A small amount of ytterbium is used to add strength to specific steel types. Ytterbium can also be used as a dopant to help improve the grain refinement, strength, and other mechanical properties of stainless steel.
Yttrium and Ytterbium – Comparison in Table
| Element | Yttrium | Ytterbium |
| Density | 6.511 g/cm3 | 6.57 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 330 MPa | 69 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 230 MPa | 66 MPa |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 88 GPa | 23.9 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | 5 | N/A |
| Brinell Hardness | 650 MPa | 340 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness | 900 MPa | 210 MPa |
| Melting Point | 1855 °C | 819 °C |
| Boiling Point | 4377 °C | 1196 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 22.7 W/mK | 39 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 5.7 µm/mK | 26.3 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.27 J/g K | 0.15 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 16.9 kJ/mol | 7.66 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 591 kJ/mol | 128.9 kJ/mol |