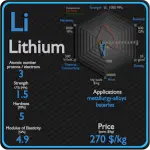
This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of sulfur and calcium, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Sulfur vs Calcium.
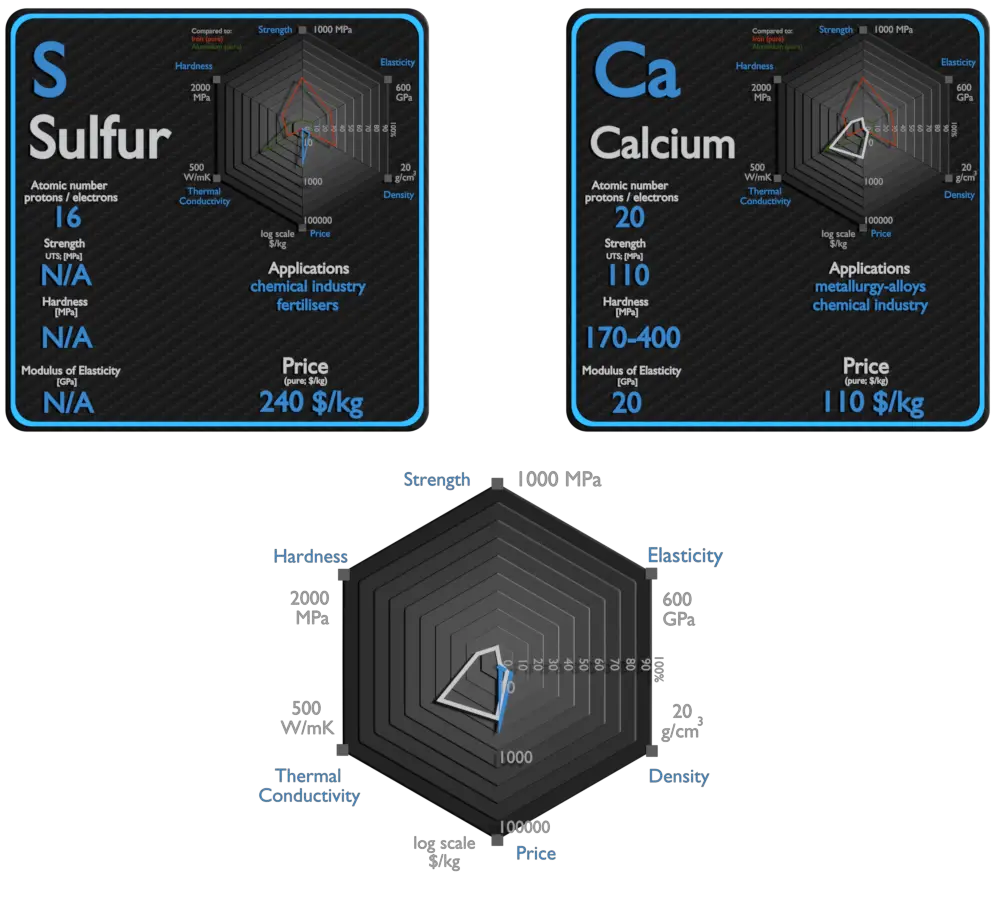
Sulfur and Calcium – About Elements

Source: www.luciteria.com
Sulfur and Calcium – Applications
Sulfur
The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of sulfuric acid for sulfate and phosphate fertilizers, and other chemical processes. Sulfur is increasingly used as a component of fertilizers. The most important form of sulfur for fertilizer is the mineral calcium sulfate. The element sulfur is used in matches, insecticides, and fungicides. Many sulfur compounds are odoriferous, and the smells of odorized natural gas, skunk scent, grapefruit, and garlic are due to organosulfur compounds.
Calcium
The largest use of metallic calcium is in steelmaking, due to its strong chemical affinity for oxygen and sulfur. Its oxides and sulfides, once formed, give liquid lime aluminate and sulfide inclusions in steel which float out. Calcium compounds are used as manufacture of insecticides, paints, blackboard chalk, textile and fireworks.
Sulfur and Calcium – Comparison in Table
| Element | Sulfur | Calcium |
| Density | 1.823 g/cm3 | 1.55 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | N/A | 110 MPa |
| Yield Strength | N/A | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | N/A | 20 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A | 170 – 400 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness | N/A | N/A |
| Melting Point | 44.1 °C | 842 °C |
| Boiling Point | 280 °C | 1484 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.235 W/mK | 200 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | N/A | 22.3 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.77 J/g K | 0.63 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 0.657 kJ/mol | 8.54 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 51.9 kJ/mol | 153.3 kJ/mol |