This article contains comparison of key thermal and atomic properties of rhodium and platinum, two comparable chemical elements from the periodic table. It also contains basic descriptions and applications of both elements. Rhodium vs Platinum.
Rhodium and Platinum – About Elements


Source: www.luciteria.com
Rhodium and Platinum – Applications
Rhodium
The element’s major use (approximately 80% of world rhodium production) is as one of the catalysts in the three-way catalytic converters in automobiles. Because rhodium metal is inert against corrosion and most aggressive chemicals, and because of its rarity, rhodium is usually alloyed with platinum or palladium and applied in high-temperature and corrosion-resistive coatings. In nuclear reactors, rhodium-based detectors are often used for incore neutron flux measuring.
Platinum
Platinum is primarily an industrial metal. It is a critical material for many industries and is considered a strategic metal. Platinum is used as a catalyst, platinum is mostly found in vehicle catalytic converters that reduce toxic exhaust chemicals, and also in fuel cells to increase efficiency. The most common use of platinum is as a catalyst in chemical reactions, often as platinum black. In catalytic converters, platinum allows the complete combustion of low concentrations of unburned hydrocarbons from the exhaust into carbon dioxide and water vapor. Platinum has been used in thermocouple devices that measure temperature with high accuracy. Platinum is a component in magnetic coatings for high-density hard disk drives and some of the newer optical storage systems.
Rhodium and Platinum – Comparison in Table
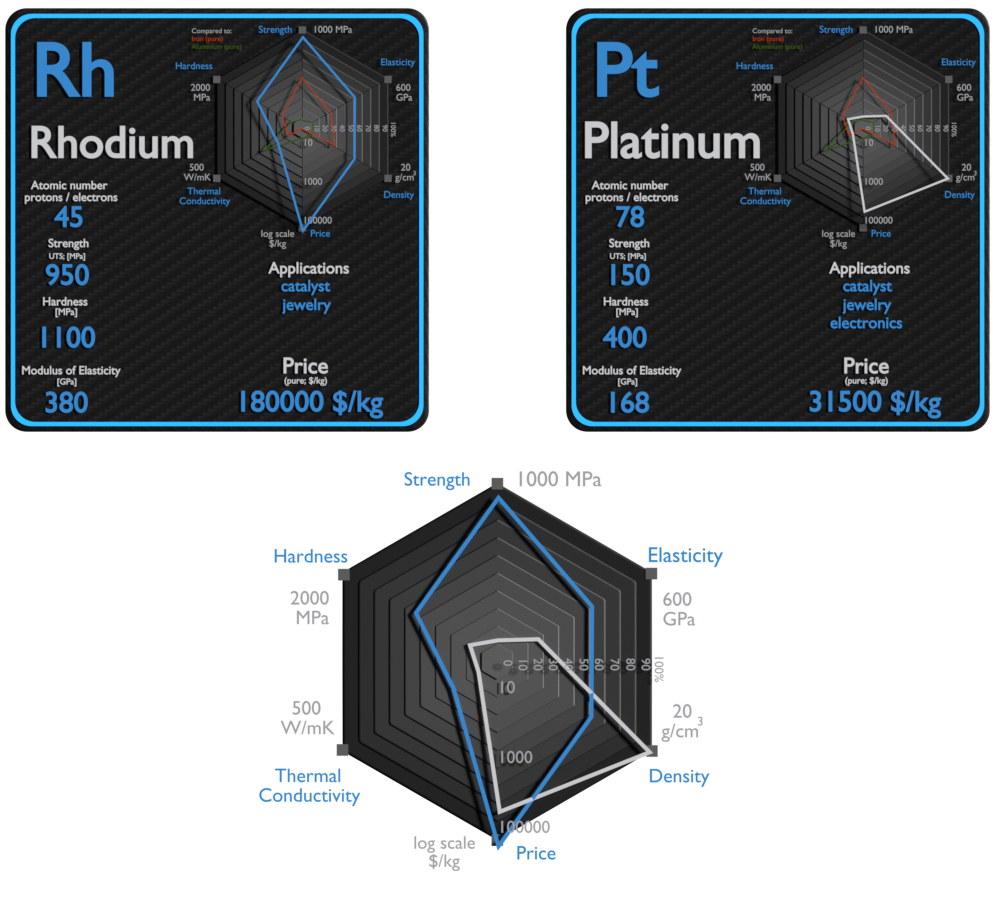
| Element | Rhodium | Platinum |
| Density | 12.45 g/cm3 | 21.09 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 950 MPa | 150 MPa |
| Yield Strength | N/A | 70 MPa |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 380 GPa | 168 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | 6 | 3.5 |
| Brinell Hardness | 1100 MPa | 400 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness | 1246 MPa | 550 MPa |
| Melting Point | 1964 °C | 1772 °C |
| Boiling Point | 3695 °C | 3827 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 150 W/mK | 72 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 8.2 µm/mK | 8.8 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.242 J/g K | 0.13 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 21.5 kJ/mol | 19.6 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 493 kJ/mol | 510 kJ/mol |








