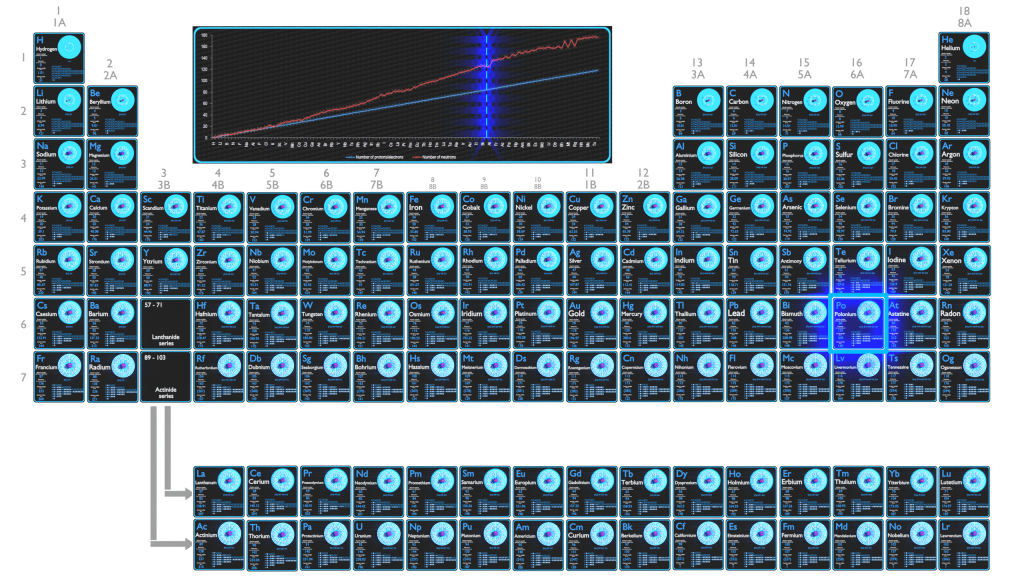
Polonium is a rare and highly radioactive metal with no stable isotopes, polonium is chemically similar to selenium and tellurium, though its metallic character resembles that of its horizontal neighbors in the periodic table: thallium, lead, and bismuth.
Protons and Neutrons in Polonium
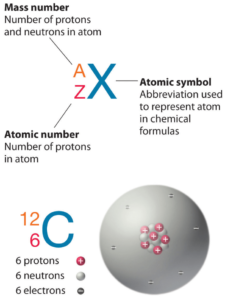 Polonium is a chemical element with atomic number 84 which means there are 84 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Polonium is a chemical element with atomic number 84 which means there are 84 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Polonium are 208-210.
Main Isotopes of Polonium
Polonium occurs naturally in 210Po, but only in traces and it is very slightly radioactive, decaying by alpha decay with a half-life of 138.376 days.
Polonium-210 is composed of 84 protons, 126 neutrons, and 84 electrons.
Naturally Occuring Isotopes
| Isotope | Abundance | Neutron Number |
| 210Po (unstable) | trace | 126 |
Typical Unstable Isotopes
| Isotope | Half-life | Decay Mode | Product |
| 208Po | 2.898 y | alpha decay and beta plus decay | 204Pb or 208Bi |
| 209Po | 125.2 y | alpha decay and beta plus decay | 205Pb or 209Bi |
| 210Po | 138.376 d | alpha decay | 206Pb |
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Polonium is 84. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration of Polonium is [Hg] 6p4.
Possible oxidation states are +2,4.
Summary
| Element | Polonium |
| Number of protons | 84 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 208-210 |
| Number of electrons | 84 |
| Electron configuration | [Hg] 6p4 |
| Oxidation states | +2,4 |
Source: www.luciteria.com