Gold is a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, from the collision of neutron stars.
Protons and Neutrons in Gold
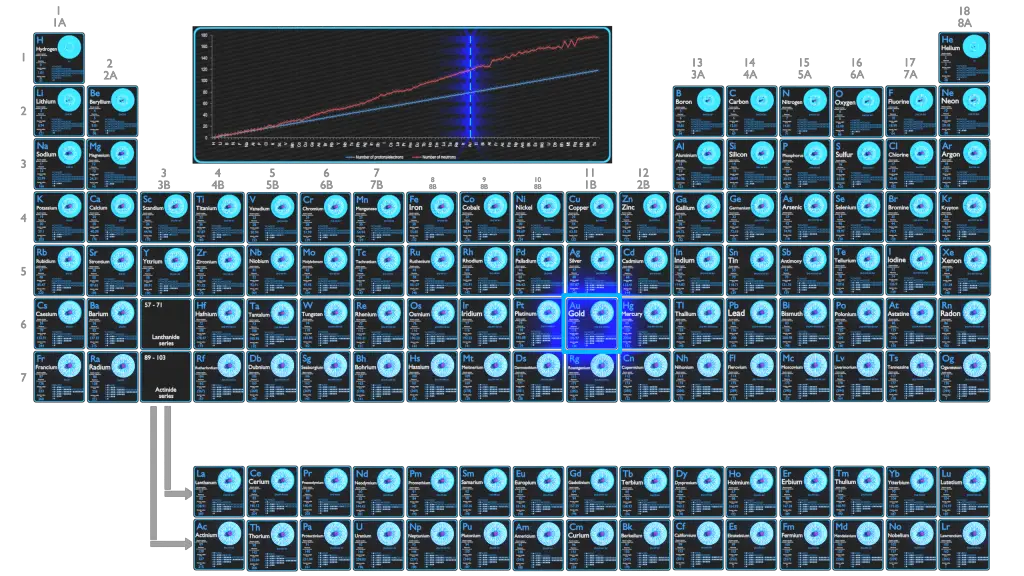
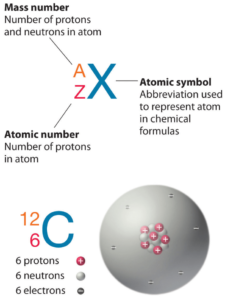 Gold is a chemical element with atomic number 79 which means there are 79 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Gold is a chemical element with atomic number 79 which means there are 79 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Gold are 197.
Main Isotopes of Gold
Gold occurs only in one natural isotope – 197Au.
Gold-197 is composed of 79 protons, 118 neutrons, and 79 electrons.
Naturally Occuring Isotopes
| Isotope | Abundance | Neutron Number |
| 197Au | 100% | 118 |
Typical Unstable Isotopes
| Isotope | Half-life | Decay Mode | Product |
| 195Au | 186.10 d | electron capture | 195Pt |
| 196Au | 6.183 d | electron capture and beta decay | 196Pt and 196Hg |
| 198Au | 2.69517 d | beta decay | 198Hg |
| 199Au | 3.169 d | beta decay | 199Hg |
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Gold is 79. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration of Gold is [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s1.
Possible oxidation states are +1,3.
Most Common Alloys of Gold
- 18K yellow gold: 75% gold, 12.5% copper, 12.5% silver
- 18K yellow (darker) gold: 75% gold, 15% copper, 10% silver
- 18K white gold: 75% gold, 25% of palladium or platinum
- 18K white gold: 75% gold, 10% palladium, 10% nickel and 5% zinc
- 18K red gold: 75% gold, 25% copper
- 18K rose gold: 75% gold, 22.25% copper, 2.75% silver
- 18K pink gold: 75% gold, 20% copper, 5% silver
- 12K red gold: 50% gold and 50% copper
Summary
| Element | Gold |
| Number of protons | 79 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 197 |
| Number of electrons | 79 |
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s1 |
| Oxidation states | +1,3 |
Source: www.luciteria.com