Terbium is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, ductile, and soft enough to be cut with a knife. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with water, evolving hydrogen gas.
Protons and Neutrons in Terbium
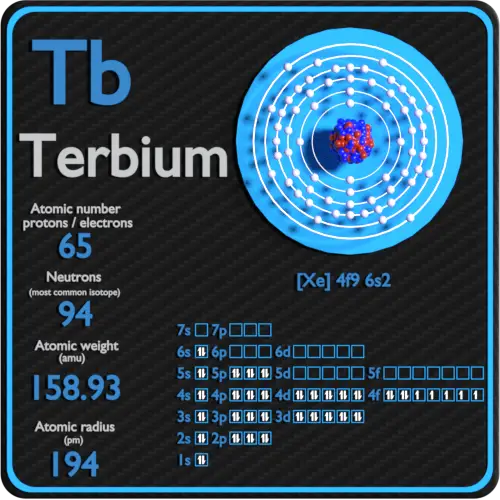
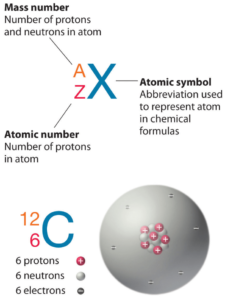 Terbium is a chemical element with atomic number 65 which means there are 65 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Terbium is a chemical element with atomic number 65 which means there are 65 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Terbium are 159.
Main Isotopes of Terbium
Terbium occurs only in one natural isotope – 159Tb.
Terbium-159 is composed of 65 protons, 94 neutrons, and 65 electrons.
Naturally Occuring Isotopes
| Isotope | Abundance | Neutron Number |
| 159Tb | 100% | 94 |
Typical Unstable Isotopes
| Isotope | Half-life | Decay Mode | Product |
| 157Tb | 71 y | electron capture | 157Gd |
| 158Tb | 180 y | electron capture | 158Gd |
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Terbium is 65. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration of Terbium is [Xe] 4f9 6s2.
Possible oxidation states are +3.
Most Common Application of Terbium
Most of the world’s terbium supply is used in green phosphors. Terbium oxide is in fluorescent lamps and television and monitor cathode ray tubes (CRTs). The most common oxidation state of terbium is +3 (trivalent), such as TbCl3. In the solid state, tetravalent terbium is also known, in compounds such as TbO2 and TbF4.
Summary
| Element | Terbium |
| Number of protons | 65 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 159 |
| Number of electrons | 65 |
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f9 6s2 |
| Oxidation states | +3 |
Source: www.luciteria.com