Aluminium is a silvery-white, soft, nonmagnetic, ductile metal in the boron group. By mass, aluminium makes up about 8% of the Earth’s crust; it is the third most abundant element after oxygen and silicon and the most abundant metal in the crust, though it is less common in the mantle below.
About 70% of commercial civil aircraft airframes are made from aluminium alloys, and without aluminium civil aviation would not be economically viable. Aluminium is extracted from the principal ore, bauxite. Significant bauxite deposits are found throughout Australia, the Caribbean, Africa, China and South America.
Protons and Neutrons in Aluminium
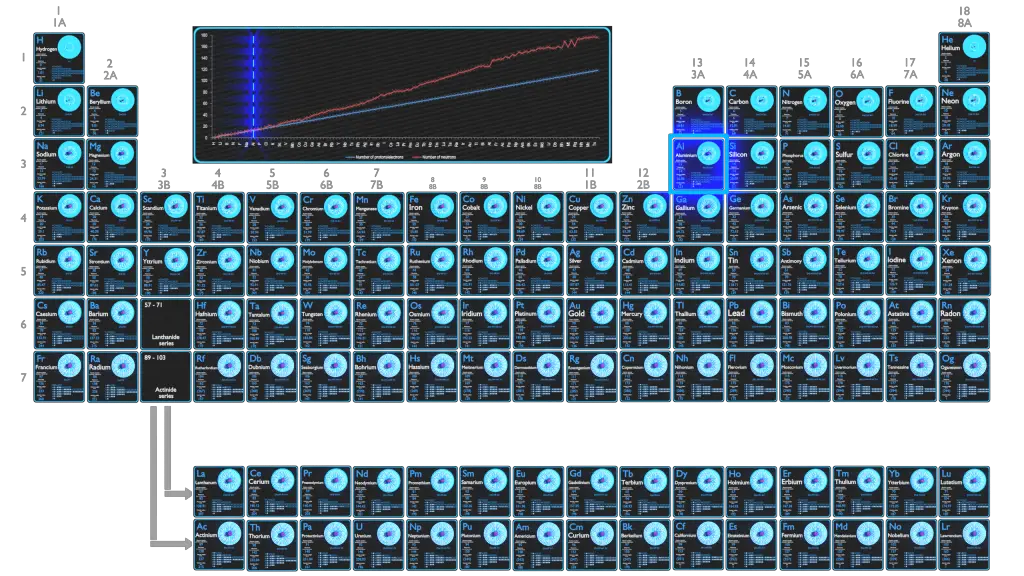
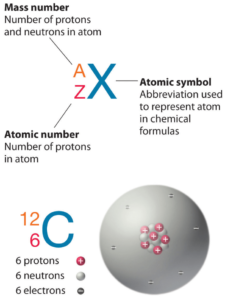 Aluminium is a chemical element with atomic number 13 which means there are 13 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Aluminium is a chemical element with atomic number 13 which means there are 13 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
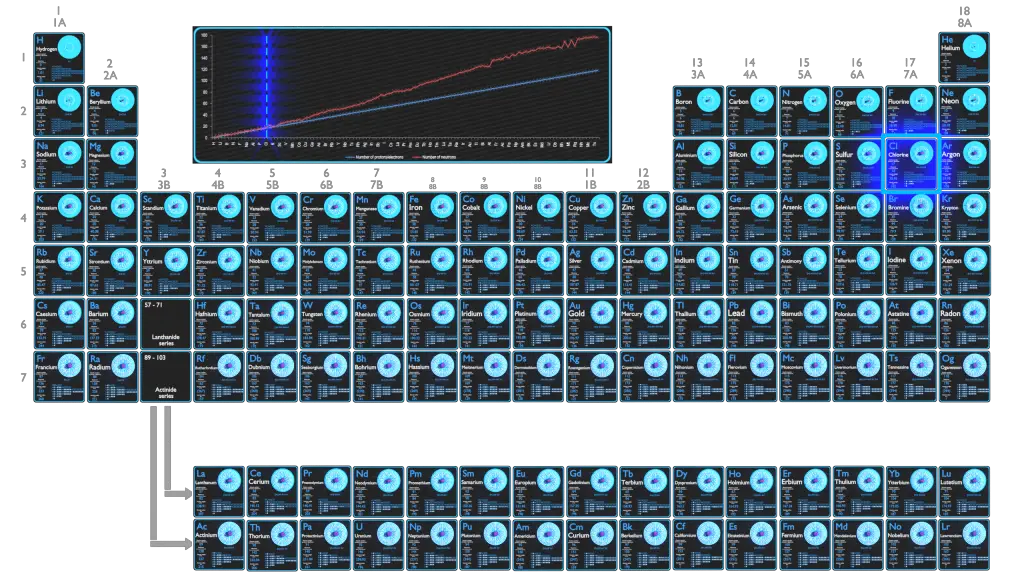
For stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Aluminium are 27.
Main Isotopes of Aluminium
Of aluminium isotopes, only 27Al is stable. This is consistent with aluminium having an odd atomic number. Only 27Al (stable isotope) and 26Al (radioactive isotope, t1/2 = 7.2×105 y) occur naturally, however 27Al comprises nearly all natural aluminium. Other than 26Al, all radioisotopes have half-lives under 7 minutes, most under a second.
Aluminium-27 is composed of 13 protons, 14 neutrons, and 13 electrons. It is the only primordial aluminium isotope, i.e. the only one that has existed on Earth in its current form since the formation of the planet. Nearly all aluminium on Earth is present as this isotope, which makes it a mononuclidic element
Aluminium-26 is composed of 13 protons, 13 neutrons, and 13 electrons. Cosmogenic aluminium-26 was first applied in studies of the Moon and meteorites. Meteorite fragments, after departure from their parent bodies, are exposed to intense cosmic-ray bombardment during their travel through space, causing substantial 26Al production. After falling to Earth, atmospheric shielding protects the meteorite fragments from further 26Al production, and its decay can then be used to determine the meteorite’s terrestrial age.
Typical Unstable Isotopes
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Aluminium is 13. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration of Aluminium is [Ne] 3s2 3p1.
Possible oxidation states are -2; -1; +1; +2; +3.
An aluminium atom has 13 electrons, arranged in an electron configuration of [Ne] 3s2 3p1, with three electrons beyond a stable noble gas configuration. Aluminium can relatively easily surrender its three outermost electrons in many chemical reactions (see below). The electronegativity of aluminium is 1.61 (Pauling scale). The vast majority of compounds, including all aluminium-containing minerals and all commercially significant aluminium compounds, feature aluminium in the oxidation state 3+. The coordination number of such compounds varies, but generally Al3+ is either six- or four-coordinate. Almost all compounds of aluminium(III) are colorless.
Most Common Aluminium Alloy
In general, 6000 series aluminium alloys are alloyed with magnesium and silicon. Alloy 6061 is one of the most widely used alloys in the 6000 Series. It has good mechanical properties, it is easy to machine, it is weldable, and can be precipitation hardened, but not to the high strengths that 2000 and 7000 can reach. It has very good corrosion resistance and very good weldability although reduced strength in the weld zone. The mechanical properties of 6061 depend greatly on the temper, or heat treatment, of the material. In comparison to 2024 alloy, 6061 is more easily worked and remains resistant to corrosion even when the surface is abraded.
About Protons
 A proton is one of the subatomic particles that make up matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making up about half of all visible matter. It has a positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c2)— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is one of the subatomic particles that make up matter. In the universe, protons are abundant, making up about half of all visible matter. It has a positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c2)— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 × 10−15 m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
The protons exist in the nuclei of typical atoms, along with their neutral counterparts, the neutrons. Neutrons and protons, commonly called nucleons, are bound together in the atomic nucleus, where they account for 99.9 percent of the atom’s mass. Research in high-energy particle physics in the 20th century revealed that neither the neutron nor the proton is not the smallest building block of matter.
About Neutrons
A neutron is one of the subatomic particles that make up matter. In the universe, neutrons are abundant, making up more than half of all visible matter. It has no electric charge and a rest mass equal to 1.67493 × 10−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton but nearly 1839 times greater than that of the electron. The neutron has a mean square radius of about 0.8×10−15 m, or 0.8 fm, and it is a spin-½ fermion.
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other through the nuclear force, while protons repel each other via the electric force due to their positive charge. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. There are only certain combinations of neutrons and protons, which forms stable nuclei.
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, because they attract each other and protons , which helps offset the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases, an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus. If there are too many or too few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is not stable and it undergoes radioactive decay. Unstable isotopes decay through various radioactive decay pathways, most commonly alpha decay, beta decay, or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such as spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known. It should be noted that all of these decay pathways may be accompanied by the subsequent emission of gamma radiation. Pure alpha or beta decays are very rare.
About Electrons and Electron Configuration
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
It is the Pauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom’s electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.
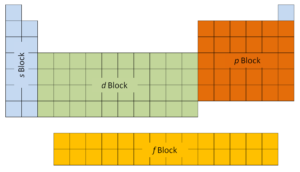 The first two columns on the left side of the periodic table are where the s subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the first two rows of the periodic table are labeled the s block. Similarly, the p block are the right-most six columns of the periodic table, the d block is the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while the f block is the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main body, but then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The first two columns on the left side of the periodic table are where the s subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the first two rows of the periodic table are labeled the s block. Similarly, the p block are the right-most six columns of the periodic table, the d block is the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while the f block is the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main body, but then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used. The electron configuration can be visualized as the core electrons, equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, and the valence electrons (e.g. [Xe] 6s2 for barium).
Oxidation States
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, zero, or negative. Most elements have more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4.
The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation state is:
“Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…”
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous. An element that is not combined with any other different elements has an oxidation state of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is simply the element in its elemental form. An atom of an element in a compound will have a positive oxidation state if it has had electrons removed. Similarly, adding electrons results in a negative oxidation state. We have also distinguish between the possible and common oxidation states of every element. For example, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4, but only -4, 0 and +4 are common oxidation states.
Summary
| Element |
Aluminium |
| Number of protons |
13 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) |
27 |
| Number of electrons |
13 |
| Electron configuration |
[Ne] 3s2 3p1 |
| Oxidation states |
-2; -1; +1; +2; +3 |

Source: www.luciteria.com
Properties of other elements
Other properties of Aluminium
 Chlorine is a chemical element with atomic number 17 which means there are 17 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Chlorine is a chemical element with atomic number 17 which means there are 17 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.