Radon is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas. Radon occurs naturally as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through which thorium and uranium slowly decay into lead.
Protons and Neutrons in Radon
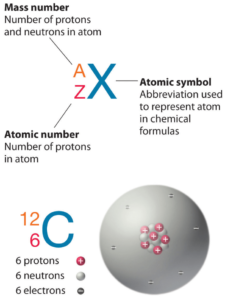 Radon is a chemical element with atomic number 86 which means there are 86 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Radon is a chemical element with atomic number 86 which means there are 86 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Radon are 222.
Main Isotopes of Radon
Radon occurs in natural form – only in isotopes 222Rn. 222Rn occur only in traces and it is very slightly radioactive, decaying by alpha decay with a half-life of 3.8235 days.
Radon-222 is composed of 86 protons, 136 neutrons, and 86 electrons.
Naturally Occuring Isotopes
| Isotope | Abundance | Neutron Number |
| 222Rn (unstable) | trace | 136 |
Typical Unstable Isotopes
| Isotope | Half-life | Decay Mode | Product |
| 210Rn | 6×104 y | alpha decay | 206Po |
| 211Rn | 14.6 h | electron capture or alpha decay | 211At or 207Po |
| 222Rn | 3.8235 d | alpha decay | 218Po |
| 224Rn | 2.4 h | beta decay | 224Fr |
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Radon is 86. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration of Radon is [Hg] 6p6.
Possible oxidation states are 0.
Summary
| Element | Radon |
| Number of protons | 86 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 222 |
| Number of electrons | 86 |
| Electron configuration | [Hg] 6p6 |
| Oxidation states | 0 |
Source: www.luciteria.com