Technetium is the lightest element whose isotopes are all radioactive; none are stable. Nearly all technetium is produced synthetically, and only minute amounts are found in the Earth’s crust. The chemical properties of this silvery gray, crystalline transition metal are intermediate between rhenium and manganese.
Protons and Neutrons in Technetium
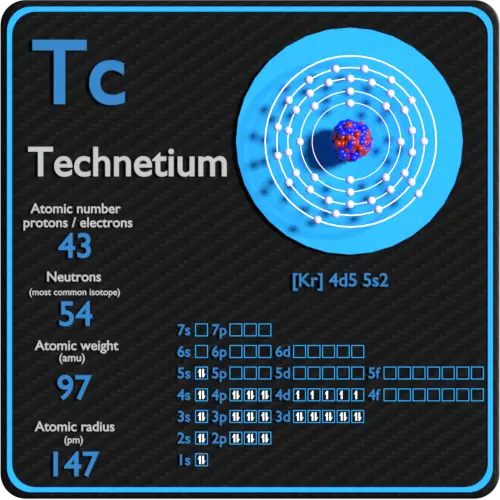
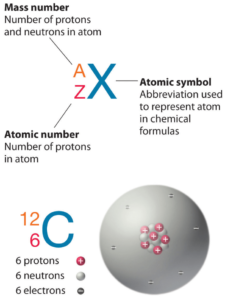 Technetium is a chemical element with atomic number 43 which means there are 43 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Technetium is a chemical element with atomic number 43 which means there are 43 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Technetium are 97-99.
Main Isotopes of Technetium
Technetium occurs in only one natural isotope – 99Tc, and only in trace amounts.
Technetium-99 is composed of 43 protons, 56 neutrons, and 43 electrons.
Naturally Occuring Isotopes
| Isotope | Abundance | Neutron Number |
| 99Tc (unstable) | trace | 56 |
Typical Unstable Isotopes
| Isotope | Half-life | Decay Mode | Product |
| 95mTc | 61 d | electron capture | 95Mo |
| 96Tc | 4.3 d | electron capture | 96Mo |
| 97Tc | 4.21×106 y | electron capture | 97Mo |
| 97mTc | 91 d | IT | 97Tc |
| 98Tc | 4.2×106 y | beta decay | 98Ru |
| 99Tc | 2.111×105 y | beta decay | 99Ru |
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Technetium is 43. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
Electron configuration of Technetium is [Kr] 4d5 5s2.
Possible oxidation states are +4,7.
Most Common Application of Technetium
One short lived gamma ray-emitting nuclear isomer, technetium-99m, is used in nuclear medicine for a wide variety of tests, such as bone cancer diagnoses.
Summary
| Element | Technetium |
| Number of protons | 43 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 97-99 |
| Number of electrons | 43 |
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d5 5s2 |
| Oxidation states | +4,7 |
Source: www.luciteria.com