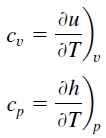——
4200 J/kg.K
Water is a wet, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth’s hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent).
The most substantial human use of water is for agriculture, including irrigated agriculture, which accounts for as much as 80 to 90 percent of total human water consumption.
——
1006 J/kg.K
Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and other trace elements. The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, commonly known as air, retained by Earth’s gravity, surrounding the planet Earth and forming its planetary atmosphere.
Air is a natural resource and is available abundantly. It is an essential element of nature that support life on earth. Air is very useful and has many applications. Uses of air are as follows: sustain life and growth, combustion, maintaining temperature, supplier of energy, photosynthesis
——
2040 J/kg.K
Ice is simply water frozen into a solid state. Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere.
Ice was used for cooling and food preservation for centuries, relying on harvesting natural ice in various forms and then transitioning to the mechanical production of the material.
——
840 J/kg.K
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent amorphous solid
Glasses have widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics.
Glass is a ubiquitous material in optics by virtue of its ability to refract, reflect, and transmit light.
——
1000 J/kg.K
Boron carbide (B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic and covalent material. It is one of the hardest materials known, ranking third behind diamond and cubic boron nitride.
Boron carbide has found application in military armour, high-performance bicycles or polishing and lapping applications. Boron carbide is also used in control rods in nuclear reactors.
——
720 J/kg.K
Graphite is a crystalline form of the element carbon. Although graphite is flexible, it is not elastic and has high electrical and thermal conductivity.
Its properties determine the variety of the areas of its applications in industry, transport, energetics, defence, medicine, science, sport.
——
800 J/kg.K
Carbon fiber is a polymer that is is a very strong material that is also very light weight. Carbon fibers have several advantages including high stiffness, high tensile strength, low weight, high chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance and low thermal expansion. Carbon fiber is five-times stronger than steel and twice as stiff.
Carbon fibers are most often used to rein rein as composite materials, especially the class of materials known as carbon fiber reinforced polymers or graphite. Carbon fibers are also used in automotive or aeronautical industry.
——
1550 J/kg.K
Polyethylene (PE) is the highest-volume polymer in the world. Its high toughness, ductility, excellent chemical resistance, low water vapor permeability, and very low water absorption, combined the ease with which it can be processed, make PE of all different density grades an attractive choice for a variety of goods.
As of 2017, over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market. PE is used to make containers, bottles, film, and pipes, among other things.
——
1700 J/kg.K
Polypropylene have properties that are similar to polyethylene, but it is slightly harder and more heat resistant. It is a white, mechanically rugged material and has a high chemical resistance. Polypropylene is recyclable.
Polypropylene is the second-most widely produced commodity plastic (after polyethylene). Polypropylene has many applications. Injection molding applications cover a broad range from automotive uses such as dome lights, kick panels, and car battery cases to luggage and washing machine parts. Filled PP can be used in automotive applications such as mounts and engine covers.
——
840 J/kg.K
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. It is relatively nontoxic and noncombustible. CO2 is a minor component of Earth’s atmosphere but important constituent of air.
CO2 is used by the food industry, the oil industry, and the chemical industry. Cooled CO2 in solid form is called dry ice. Carbon dioxide also is used as a refrigerant, in fire extinguishers, for inflating life rafts and life jackets, blasting coal, foaming rubber and plastics, promoting the growth of plants in greenhouses.
——
800 J/kg.K
Bricks are structural clay products, manufactured as standard units. Three basic types of brick are un-fired, fired, and chemically set bricks. Each type is manufactured differently.
Bricks are most often used for both buildings and pavements. Bricks in the metallurgy and glass industries are often used for lining furnaces, in particular refractory bricks such as silica, magnesia, chamotte and neutral (chromomagnesite) refractory bricks.
——
1050 J/kg.K
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating materials, generally including a material like kaolin, in a kiln to temperatures between 1,200 and 1,400 °C. Porcelain and stoneware materialsare about as resistant to acids and chemicals as glass, but with greater strength.
Porcelain can be used as a building material, usually in the form of tiles or large rectangular panels. Porcelain and other ceramic materials have many applications in engineering, especially ceramic engineering. It is an excellent insulator for use with high voltages, especially in outdoor applications.
——
292 J/kg.K
Tungsten carbide is a very dense carbide containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms.
In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed for use in industrial machinery, cutting tools, abrasives, armor-piercing shells and jewellery. Tungsten carbide is used extensively in mining in top hammer rock drill bits, downhole hammers, roller-cutters, long wall plough chisels, long wall shearer picks, raiseboring reamers, and tunnel boring machines. The cemented composites of tungsten carbide-cobalt are known by many different trade names, including Widia and Carboloy.
——
509 J/kg.K
Diamond is a form of carbon amd it is the hardest naturally occurring material known. Yet, due to important structural weaknesses, diamond’s toughness is only fair to good.
The most familiar uses of diamonds today are as gemstones used for adornment, and as industrial abrasives for cutting hard materials. The markets for gem-grade and industrial-grade diamonds value diamonds differently. In industry, diamonds applications include oil drilling bits, rock drill cutters, wire drawing dies, extrusion dies, cutting tool inserts, optical grinding tools, coatings for computer hard discs and coatings for ball bearings.
——
N/A
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon. Graphene has high thermal conductivity, high electrical conductivity, high elasticity and flexibility, high hardness and strength.
Graphene is a transparent and flexible conductor that holds great promise for various material/device applications, including solar cells, light-emitting diodes (LED), touch panels, and smart windows or phones. Smartphone products with graphene touch screens are already on the market.
——
1250 J/kg.K
Polyethylene terephthalate, commonly abbreviated PET, PETE, is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family. PET is a hard, stiff, strong, dimensionally stable material that absorbs very little water.
Typical using of PET is as an injection-molding-grade material, for blow-molded bottles, and for oriented films. The majority of the world’s PET production is for synthetic fibers (in excess of 60%), with bottle production accounting for about 30% of global demand.
——
1200 J/kg.K
Polycarbonate (PC) is a thermoplastic polymer. It is a crystal clear and colourless, but it has a weakness to notches.
Polycarbonate is mainly used for electronic applications, it is used in various products associated with electrical and telecommunications hardware. A major application of polycarbonate is the production of Compact Discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray Discs. It is also used in safety helmets, riot shields, aircraft canopies, traffic light lens housings, and automotive battery cases.
——
1040 J/kg.K
Carbon monoxide, (CO), a highly toxic, colourless, odourless, flammable gas. Carbon monoxide is not found in the air under ordinary conditions, since it is formed by incomplete carbon combustion of coal, natural gas, oil.
CO is produced industrially for use in the manufacture of numerous organic and inorganic chemical products such as acids, esters and alcohol or it is used in fuel gas mixtures with hydrogen and other gases for industrial and domestic heating.
——
830 J/kg.K
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles. The composition of sand varies, depending on the local rock sources and conditions.
Sand is a non-renewable resource over human timescales, and sand suitable for making concrete is in high demand. In the pottery and glassmaking industries very pure quartzose sands are used as a source of silica. Similar sands are required for lining the hearths of acid-steel furnaces.
——
840 J/kg.K
Limestone is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock.
Limestone is very common in architecture, especially in Europe and North America. Limestone is extracted from quarries or mines. The principal users of lime are steelmaking industry (lowering slag melting temperature) ~ 35 %, environmental uses (desulfurization, water cleaning) ~ 20 %, civil engineering ~ 20 % and chemistry ~ 8 %.
——
900 J/kg.K
In general, Elektron is the registered trademark of a wide range of magnesium alloys manufactured by a British company Magnesium Elektron Limited. Elektron 21, designated by UNS M12310, is one of alloys with excellent corrosion resistance and castability.
Application include motorsports and aerospace, since it possess high strength, light weight and it has excellent vibration damping characteristics.
——
900 J/kg.K
Duralumin (also called duraluminum, duraluminium, duralum, dural(l)ium, or dural) is a strong, lightweight alloy of aluminium discovered in 1910 by Alfred Wilm, a German metallurgist. He discovered that after quenching, an aluminium alloy containing 4% copper would slowly harden when left at room temperature for several days. This process is now known as natural aging.
The alloy can be rolled, forged and extruded into various forms and products. The light weight and high strength of duralumin when compared to steel enabled its application in aircraft construction.
——
285 J/kg.K
Zirconium alloys, in which tin is the basic alloying element, provides improvement of their mechanical properties, have a wide distribution in the USA. A common subgroup has the trade mark Zircaloy. In case of zirconium-tin alloys, the decrease of corrosion resistance in water and steam is taken place that resulted in the need for additional alloying.
——
500 J/kg.K
Austenitic stainless steels have the best corrosion resistance of all stainless steels and they have excellent cryogenic properties, and good high-temperature strength. They possess a face-centered cubic (fcc) microstructure that is nonmagnetic, and they can be easily welded.Type 304 stainless steel (containing 18%-20% chromium and 8%-10.5% nickel) is the most common stainless steel. It is also known as “18/8” stainless steel because of its composition, which includes 18% chromium and 8% nickel. This alloy resists most types of corrosion.
——
510 J/kg.K
Low-carbon steel contains approximately 0.05–0.25% carbon making it malleable and ductile. Mild steel has a relatively low tensile strength, but it is cheap and easy to form; surface hardness can be increased through carburizing.
Typical applications include automobile body components, structural shapes (e.g., I-beams, channel and angle iron), and sheets that are used in pipelines, buildings.
——
460 J/kg.K
Gray cast iron is the oldest and most common type of iron in existence and probably what most people think of when they hear the term “cast iron”. Gray cast iron has less tensile strength and shock resistance than steel, but its compressive strength is comparable to low- and medium-carbon steel. Gray cast iron has good thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity, therefore it is often used in cookware and brake rotors.
——
305 J/kg.K
Molybdenum-titanium-zirconium (TZM) alloys contain small amounts of titanium and zirconium doped with small amounts of very fine carbides. Key requirement to withstand high temperatures is a high melting point and stable mechanical properties (e.g. high hardness) even at high temperatures.TZM alloys are used in virtually all major industries, where high temperature applications with heavy mechanical load is required. For example, aerospace, automotive, chemicals, mining, nuclear technology and metal processing. It is typically manufactured by powder metallurgy or arc-casting processes.
——
460 J/kg.K
Inconel 718 is a nickel-based superalloy that possesses high strength properties and resistance to elevated temperatures. It also demonstrates remarkable protection against corrosion and oxidation. Inconel’s high temperature strength is developed by solid solution strengthening or precipitation hardening, depending on the alloy. Inconel 718 is composed of 55% nickel, 21% chromium, 6% iron, and small amounts of manganese, carbon, and copper.
——
380 J/kg.K
Electrolytic tough pitch copper, UNS C11000, is pure copper (with a maximum of 0.0355% of impurities) refined by electrolytic refining process and it is the most widely used grade of copper all over the world.
Electrical wiring is the most important market for the copper industry. This includes structural power wiring, power distribution cable, appliance wire, communications cable, automotive wire and cable, and magnet wire.
——
400 J/kg.K
Cupronickels are copper-nickel alloys that contain typically from 60% to 90% of copper and nickel as the main alloying element. The two main alloys are 90/10 and 70/30. Other strengthening elements, such as manganese and iron, may be also contained. Cupronickels have excellent resistance to corrosion caused by sea water.
Cupronickels may be used in many marine applications, such as for the propellers and propeller shafts.
——
420 J/kg.K
Zamak is a family of alloys with a base metal of zinc and alloying elements of aluminium, magnesium, and copper. Zinc alloys have low melting points, require relatively low heat input, do not require fluxing or protective atmospheres. Because of their high fluidity, zinc alloys can be cast in much thinner walls than other die castings alloys, and they can be die cast to tighter dimensional tolerances.
——
750 J/kg.K
A ruby is a pink to blood-red coloured gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum (aluminium oxide). Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires.
Like other gemstones, rubies are becoming an increasingly popular choice for engagement rings and other jewelry.
——
235 J/kg.K
Uranium dioxide is a ceramic refractory uranium compound, in many cases used as a nuclear fuel. Uranium dioxide is a black semiconducting solid with very low thermal conductivity, but it has very high melting point and has well known behavior. Uranium dioxide has significantly lower density than uranium in the metal form.
Most of LWRs use the uranium fuel, which is in the form of uranium dioxide (chemically UO2)
——
1100 J/kg.K
Polystyrene, abbreviated as PS, is a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer made from the monomer known as styrene. PS can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and rather brittle. It is a colorless and transparent thermoplastic.
PS is one of the four plastics whose combined usage accounts for 75% of the worldwide usage of plastics (PE, PP, PVC, and PS). Applications include toys, light diffusers, beakers, cutlery, general household appliances, video/audio cassette cases, electronic housings, refrigerator liners, housewares, containers.
——
880 J/kg.K
Polyvinyl chloride is the world’s third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer. There are two basic forms of PVC: rigid and plasticized. About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC is one of the four plastics whose combined usage accounts for 75% of the worldwide usage of plastics (PE, PP, PVC, and PS).
Rigid PVC products include house siding, extruded pipe, thermoformed, and injectionmolded parts. Rigid PVC is calendered into credit cards. Plasticized PVC is used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, imitation leather, flooring, signage, phonograph records.
——
880 J/kg.K
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or nitrous, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N2O. Nitrous oxide is a naturally occurring gas that is colorless and non flammable.
Nitrous oxide can be manufactured and used for a variety of things such as a pharmacologic agent to produce anesthesia, a food additive as a propellant, and an additive to fuels to increase available oxygen in combustion. Nitrous oxide may be used as an oxidiser in a rocket motor. In vehicle racing, nitrous oxide allows the engine to burn more fuel by providing more oxygen during combustion.
——
1050 J/kg.K
Concrete is a composite material made from sand, gravel and cement.
Concrete is one of the most frequently used building materials. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminum combined. Most concrete is poured with reinforcing materials (such as rebar) embedded to provide tensile strength, yielding reinforced concrete.
——
790 J/kg.K
Granite is a coarse-grained igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase.
Granite has been extensively used as a dimension stone and as flooring tiles in public and commercial buildings and monuments.
——
520 J/kg.K
Commercially pure titanium grade 2 is very similar to grade 1, but it has higher strength than grade 1 and excellent cold forming properties. It provides excellent welding properties and has excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion. This grade of titanium is the most common grade of the commercially pure titanium industry.
Aerospace applications, including use in both structural (airframe) components and jet engines, still account for the largest share of titanium alloy use. Due to very high inertness, titanium has many biomedical applications, which is based on its inertness in the human body, that is, resistance to corrosion by body fluids.
——
896 J/kg.K
In general, 6000 series aluminium alloys are alloyed with magnesium and silicon. Alloy 6061 is one of the most widely used alloys in the 6000 Series. It has good mechanical properties, it is easy to machine, it is weldable, and can be precipitation hardened, but not to the high strengths that 2000 and 7000 can reach.
Applications range from aircraft components (aircraft structures, such as wings and fuselages) to automotive parts such such as the chassis of the Audi A8.
——
285 J/kg.K
Zirconium alloys with niobium are used as claddings of fuel elements of VVER and RBMK reactors. These alloys are the basis material of assembly channel of RBMK reactor. The Zr + 1% Nb alloy of type N-1 E-110 is used for fuel element claddings, the Zr + 2.5% Nb alloy of type E-125 is applied for tubes of assembly channels.
——
460 J/kg.K
Martensitic stainless steels are similar to ferritic steels in being based on chromium but have higher carbon levels up as high as 1%. They have moderate corrosion resistance, but are considered hard, strong, slightly brittle.
Grade 440C stainless steel is used in the following applications: gage blocks, cutlery, ball bearings and races, molds and dies, knives.
——
490 J/kg.K
High-carbon steel has approximately 0.60 to 1.00% carbon content. Hardness is higher than the other grades but ductility decreases. They are almost always used in a hardened and tempered condition and, as such, are especially wear resistant and capable of holding a sharp cutting edge.
——
540 J/kg.K
White cast irons are hard, brittle, and unmachinable, while gray irons with softer graphite are reasonably strong and machinable. A fracture surface of this alloy has a white appearance, and thus it is termed white cast iron.
——
220 J/kg.K
Molybdenum and rhenium are both refractory metals. Molybdenum-rhenium alloys offer high temperature strength; the combination drastically increases ductility and tensile strength.
The molybdenum-rhenium alloys exhibiting good low-temperature ductility. Rhenium is gaining acceptance in nuclear reactors, rockets, and other commercial and aerospace applications.
——
420 J/kg.K
Hastelloy is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium wrought superalloy that is generally considered a versatile corrosion-resistant alloy. This alloy resists the formation of grain-boundary precipitates in the weld heat affected zone, thus making it suitable for most chemical process applications in the as-welded condition. Super alloys have good oxidation and creep resistance and can be strengthened by precipitation hardening, solid-solution hardening and work hardening methods.
Hastelloy is widely used is used for desulphurization of flue gas equipment and for chemical process equipment.
——
380 J/kg.K
Brass is is the generic term for a range of copper-zinc alloys. Brass can be alloyed with zinc in different proportions, which results in a material of varying mechanical, corrosion and thermal properties.
Some of the common uses for brass alloys include costume jewelry, locks, hinges, gears, bearings, hose couplings, ammunition casings, automotive radiators, musical instruments, electronic packaging, and coins.
——
380 J/kg.K
The aluminum bronzes are a family of copper-based alloys offering a combination of mechanical and chemical properties unmatched by any other alloy series. They contain about 5 to 12% of aluminium. They have excellent strength, similar to that of low alloy steels, and excellent corrosion resistance especially in seawater and similar environments, where the alloys often outperform many stainless steels.
——
167 J/kg.K
In electronics assembly, the eutectic alloy with 63% tin and 37% lead (or 60/40, which is almost identical in melting point) has been the alloy of choice. This eutectic alloy has melting point lower than those of either tin or lead.
——
880 J/kg.K
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). Salt in its natural form as a crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on inclusion of other materials, impurities, and structural or isotopic abnormalities in the crystals.
Salt has many uses. Most of the salt produced is crushed and used in the winter on roads to control the accumulation of snow and ice. Significant amounts of salt are also used by the chemical industry. Salt is an essential nutrient for humans and most animals, and it is also a favorite seasoning for many types of food.
——
1420 J/kg.K
Aramid fiber is an aromatic polyamide, which is better known by tradenames such as Kevler (DuPont) and Twaron (Teijin Twaron). Kevlar fibers have tensile strength and high thermal stability.
Kevlar has many applications, ranging from bicycle tires and racing sails to bulletproof vests, because of its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio; by this measure it is five times stronger than steel. The high tenacity and thermally stable fibers are used for lightweight bulletproof body armor, and also due to weight-saving it can also replace heavier materials in airplanes, for fuel saving.
——
1500 J/kg.K
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Nylon is a crystalline polymer with high modulus, strength, and impact properties, and low coefficient of friction and resistance to abrasion. Nylon fibers do have a tendency to pick up a static charge, so antistatic agents are often added for carpeting and other applications.
Nylons can be used as gears, cams, rollers, bearings, nuts and bolts, power tool housings, electrical connectors, combs, coil formers, fuel tanks for cars, kitchen utensils.
——
1300 J/kg.K
Rubber is a material, which can stretch and shrink. It is a polymer. It can be produced from natural sources (e.g. natural rubber) or can be synthesised on an industrial scale. Natural rubber, also called caucho or caoutchouc.
Rubber moulded products are widely used industrially (and in some household applications) in the form of rubber goods and appliances. Rubber is used in garden hoses and pipes for small scale gardening applications. For example, car tires are usually made from Styrene-butadiene or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). In 2012, more than 5.4 million tonnes of SBR were processed worldwide.
——
2200 J/kg.K
Methane, CH4, is a colorless odorless gas. It is also known as marsh gas or methyl hydride. The vapors are lighter than air. It is a group-14 hydride and the simplest alkane, and is the main constituent of natural gas.
Methane is a fuel and can be used in industrial chemical processes and may be transported as a refrigerated liquid (liquefied natural gas, or LNG). Methane is used as a fuel for ovens, homes, water heaters, kilns, automobiles, turbines, and other things.
——
700 J/kg.K
Stone wool, also known as rock wool, is based on natural minerals present in large quantities throughout the earth, e.g. volcanic rock, typically basalt or dolomite. It combines mechanical resistance with good thermal performance, fire safety and high temperature suitability.
Applications of stone wool include structural insulation pipe insulation, filtration, soundproofing, and hydroponic growth medium. Stone wool is a versatile material that can be used for the insulation of walls, roofs and floors.
——
741 J/kg.K
Quartz is very abundant mineral of many varieties that consists primarily of silica, or silicon dioxide (SiO2).
Quartz has great economic importance. Many varieties are gemstones, including amethyst, citrine, smoky quartz, and rose quartz. It has electrical properties (e.g. its piezoelectricity) and heat resistance that make it valuable in electronic products. Sandstone, composed mainly of quartz, is an important building stone. Large amounts of quartz sand (also known as silica sand) are used in the manufacture of glass and ceramics and for foundry molds in metal casting. Crushed quartz is used as an abrasive in sandpaper, silica sand is employed in sandblasting.
——
560 J/kg.K
Grade 5 is the most commonly used alloy and it is an alpha + beta alloy. Grade 5 alloy accounts for 50% of total titanium usage the world over. It has a chemical composition of 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium, 0.25% (maximum) iron, 0.2% (maximum) oxygen, and the remainder titanium. Generally, Ti-6Al-4V is used in applications up to 400 degrees Celsius.
——
1050 J/kg.K
7068 aluminium alloy is a heat treatable wrought alloy with good fatigue strength, good anodizing response, and high thermal conductivity. It is alloyed with zinc, magnesium and copper. 7068 aluminium alloy is one of the strongest commercially available aluminium alloys, with a tensile strength comparable to that of some steels.
Alloy 7068 is now being used or considered for markets like the aerospace and automotive industries (valve body and connecting rod applications), medical devices, such as prosthetic limbs, as well as recreational products like bicycles and mountain-climbing equipment.
——
477 J/kg.K
Chromoly steel is medium-carbon ultrahigh-strength low alloy steel that gets its name from a combination of the words “chromium” and “molybdenum” – two of the major alloying elements. Chromoly steel is often used when more strength is required than that of mild carbon steel, though it often comes at an increase in cost.
——
460 J/kg.K
Duplex stainless steels, as their name indicates, are a combination of two of the main alloy types. They have a mixed microstructure of austenite and ferrite, the aim usually being to produce a 50/50 mix, although in commercial alloys the ratio may be 40/60.
——
465 J/kg.K
Tool steel refers to a variety of carbon and alloy steels that are particularly well-suited to be made into tools (punches, dies, molds, tools for cutting, blanking, forming, drawing, steering and slitting tools). With a carbon content between 0.5% and 1.5%, tool steels are manufactured under carefully controlled conditions to produce the required quality.
——
460 J/kg.K
Ductile iron is stronger and more shock resistant than gray iron, so although it is more expensive due to alloyants, it may be the preferred economical choice because a lighter casting can perform the same function.
Typical applications for this material include valves, pump bodies, crankshafts, gears, and other automotive and machine components because of its good machinability, fatigue strength, and higher modulus of elasticity.
——
140 J/kg.K
Tungsten and rhenium are both refractory metals. These metals are well known for their extraordinary resistance to heat and wear. Powder-metallurgy methods can be used in consolidating tungsten-rhenium alloys. Tungsten-rhenium alloys offer the highest temperature strength of any metal.
Historically Tungsten 25% Rhenium alloy has been produced into wire for the thermocouple market.The applications for these materials are in the joining, medical, aerospace, furnace, and heat treat industries. Rhenium is gaining acceptance in nuclear reactors, miniature rockets, and other commercial and aerospace applications.
——
423 J/kg.K
Stellite alloys are a group of cobalt-chromium ‘super-alloys’ consisting of complex carbides in an alloy matrix predominantly designed for high wear resistance and superior chemical and corrosion performance in hostile environments. Cobalt-base alloys are characterized by a solid-solution-strengthened austenitic (fcc) matrix in which a small quantity of carbide is distributed.
Typical applications include saw teeth, hardfacing, and acid-resistant machine parts. Stellite was a major improvement in the production of poppet valves and valve seats for the valves, particularly exhaust valves, of internal combustion engines.
——
435 J/kg.K
In general, bronzes are a family of copper-based alloys traditionally alloyed with tin, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin. The addition of small amounts (0.01–0.45) of phosphorus further increases the hardness, fatigue resistance and wear resistance.
Addition of these alloyants leads to applications such as springs, fasteners, masonry fixings, shafts, valve spindles, gears and bearings.
——
420 J/kg.K
Copper beryllium, also known as beryllium bronze, is a copper alloy with 0.5—3% beryllium. Copper beryllium is the hardest and strongest of any copper alloy (UTS up to 1,400 MPa), in the fully heat treated and cold worked condition. It combines high strength with non-magnetic and non-sparking qualities.
——
210 J/kg.K
An amalgam is an alloy of mercury with another metal. It may be a liquid, a soft paste or a solid, depending upon the proportion of mercury.
Silver-mercury amalgams are important in dentistry, and gold-mercury amalgam is used in the extraction of gold from ore. Dentistry has used alloys of mercury with metals such as silver, copper, indium, tin and zinc.
——
1244 J/kg.K
Sugar is colourless, water-soluble compound present in the sap of seed plants and the milk of mammals and making up the simplest group of carbohydrates.
The most common sugar is sucrose, a crystalline tabletop and industrial sweetener. Sucrose is used in prepared foods (e.g. cookies and cakes), is sometimes added to commercially available processed food and beverages, and may be used by people as a sweetener for foods (e.g. toast and cereal) and beverages (e.g. coffee and tea). The average person consumes about 24 kilograms (53 lb) of sugar each year
——
2200 J/kg.K
In general, waxes are a diverse class of organic compounds that are lipophilic, malleable solids near ambient temperatures. Although many natural waxes contain esters, paraffin waxes are hydrocarbons, mixtures of alkanes usually in a homologous series of chain lengths. These materials represent a significant fraction of petroleum.
Waxes are mainly consumed industrially as components of complex formulations, often for coatings. Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication, electrical insulation, and candles. Dyed paraffin wax can be made into crayons.
——
1380 J/kg.K
Coal is a rock formed from the decomposition of plant life. It is primarily composed of carbon, with many other trace elements.
About 8000 Mt of coal are produced annually, about 90% of which is hard coal and 10% lignite. As of 2018 just over half is from underground mines. The most significant uses of coal are in electricity generation, steel production, cement manufacturing and as a liquid fuel.
——
900 J/kg.K
Asphalt, also known as bitumen, is black or brown petroleum-like material that has a consistency varying from viscous liquid to glassy solid. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Asphalt consists of compounds of hydrocarbons.
The primary use (70%) of asphalt is in road construction, where it is used as the glue or binder mixed with aggregate particles to create asphalt concrete. Its other main uses are for bituminous waterproofing products, including production of roofing felt and for sealing flat roofs.
——
1630 J/kg.K
Propane is a colourless, easily liquefied, gaseous hydrocarbon (alkane). It is separated in large quantities from natural gas, light crude oil, and oil-refinery gases.
Propane is commonly used as a fuel in domestic and industrial applications and in low-emissions public transportation. It is commercially available as liquefied propane or as a major constituent of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
——
840 J/kg.K
Glass wool (originally known also as fiberglass) is an insulating material made from fibers of glass arranged using a binder into a texture similar to wool. Glass wool and stone wool are produced from mineral fibers and are therefore often referred to as ‘mineral wools’.
Applications of glass wool include structural insulation, pipe insulation, filtration and soundproofing. Glass wool is a versatile material that can be used for the insulation of walls, roofs and floors. It can be a loose fill material, blown into attics, or, together with an active binder sprayed on the underside of structures.
——
1900 J/kg.K
Aerogel is a synthetic porous ultralight solid material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component of the gel has been replaced with a gas (during a supercritical drying process). Aerogels can be made from a variety of chemical compounds, but the base material for aerogel is usually silicon.
In 2004 about US$25 million of aerogel insulation product were sold, which had risen to about US$500 million by 2013.The potential to replace conventional insulation with aerogel solutions in the building and construction sector as well as in industrial insulation is quite significant. NASA used an aerogel to trap space dust particles aboard the Stardust spacecraft.
——
230 J/kg.K
Pure gold is a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, from the collision of neutron stars. Rose gold is a gold–copper alloy widely used for specialized jewelry.
Gold is used extensively in jewellery (about 75% of all world production), either in its pure form or as an alloy. The term ‘carat’ indicates the amount of gold present in an alloy. 24-carat is pure gold, but it is very soft. 18- and 9-carat gold alloys are commonly used because they are more durable.
——
200 J/kg.K
Pure gold is a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, from the collision of neutron stars. Yellow gold is usually pure gold, but in jewelry gold alloys widely are used to increase strength of pure metal.
Gold is used extensively in jewellery (about 75% of all world production), either in its pure form or as an alloy. The term ‘carat’ indicates the amount of gold present in an alloy. 24-carat is pure gold, but it is very soft. 18- and 9-carat gold alloys are commonly used because they are more durable.
——
220 J/kg.K
Pure gold is a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold is thought to have been produced in supernova nucleosynthesis, from the collision of neutron stars. White gold is a gold–silver (or nickel or palladium) alloy.
Gold is used extensively in jewellery (about 75% of all world production), either in its pure form or as an alloy. The term ‘carat’ indicates the amount of gold present in an alloy. 24-carat is pure gold, but it is very soft. 18- and 9-carat gold alloys are commonly used because they are more durable.
——
460 J/kg.K
PH stainless steels (precipitation-hardening) contain around 17% chromium and 4% nickel. Precipitation-hardening stainless steels have high toughness, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Precipitation-hardening stainless steels have been increasingly used for a variety of applications in marine construction, aircraft and gas turbines, chemical industries and nuclear power plants.
——
470 J/kg.K
High-speed steels, abbreviated as HSS, are a specialized class of tool steels that were named primarily for their ability to machine and cut materials at high speeds (high hot hardness).High-speed steels are complex iron-base alloys of carbon, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, or tungsten, or combinations there of. To achieve good cutting performance from HSS, an appropriate hardening response must be provided in heat treatment.
——
465 J/kg.K
Malleable cast iron is white cast iron that has been annealed. Through an annealing heat treatment, the brittle structure as first cast is transformed into the malleable form. Therefore, its composition is very similar to that of white cast iron, with slightly higher amounts of carbon and silicon.
——
130 J/kg.K
Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in chemical compounds. Tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material, making it difficult to work.
Tungsten is widely used metal. Approximately half of the tungsten is consumed for the production of hard materials – namely tungsten carbide – with the remaining major use being in alloys and steels. The remaining 40% is generally used to make various alloys and specialty steels, electrodes, filaments, wires, as well as diverse components for electric, electronic, heating, lighting, and welding applications.
——
505 J/kg.K
Invar is an alloy of nickel and iron. This alloy is also known generically as FeNi36 (64FeNi in the US). Invar is notable for its uniquely low coefficient of thermal expansion.
Invar was formerly used for absolute standards of length measurement and is now used for surveying tapes and in watches and various other temperature-sensitive devices. Invar is used where high dimensional stability is required, such as precision instruments, clocks, seismic creep gauges, television shadow-mask frames, valves in engines and large aerostructure molds.
——
390 J/kg.K
Constantan is a copper–nickel alloy consisting usually of 55% copper and 45% nickel and specific minor amounts of additional elements to achieve precise (almost constant) values for the temperature coefficient of resistivity. That means, its main feature is the low thermal variation of its resistivity, which is constant over a wide range of temperatures. Other alloys with similarly low temperature coefficients are known, such as manganin.
Constantan is used for the measurement of temperature, the formation of thermocouple or resistance purpose.
——
377 J/kg.K
Nickel silver, known also as German silver, nickel brass or alpacca, is a copper alloy with nickel and often zinc. UNS C75700 nickel silver 65-12 copper alloy has good corrosion and tarnish-resistance, and high formability. Nickel silver is named due to its silvery appearance, but it contains no elemental silver unless plated.
Nickel silver alloys are used for decorative applications, jewellery, model making, musical instruments (e.g., flutes, clarinets), flutes ball point refills, screws, rivets and fishing rods, test probes.
——
296 J/kg.K
Galinstan is a eutectic alloy composed of gallium, indium, and tin (hence its name, which is derived from the gallium, indium, and stannum, the Latin name for tin).
Due to the low toxicity and low reactivity of its component metals, in many applications, galinstan has replaced the toxic liquid mercury or the reactive NaK (sodium–potassium alloy). Metals or alloys like galinstan that are liquids at room temperature are often used by overclockers and enthusiasts as a thermal interface for computer hardware cooling.
——
2000 J/kg.K
Wood is an organic material – a natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. It is common to classify wood as either softwood or hardwood. The wood from conifers (e.g. pine) is called softwood, and the wood from dicotyledons (usually broad-leaved trees, e.g. oak) is called hardwood.
Oak wood is very resistant to insect and fungal attack because of its high tannin content. In Medieval Europe oak was the wood of choice for all wood construction, including beams, walls, doors, and floors.
——
2300 J/kg.K
Wood is an organic material – a natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. It is common to classify wood as either softwood or hardwood. The wood from conifers (e.g. pine) is called softwood, and the wood from dicotyledons (usually broad-leaved trees, e.g. oak) is called hardwood.
Pines are among the most commercially important tree species valued for their timber and wood pulp throughout the world. Some species have large seeds, called pine nuts, that are harvested and sold for cooking and baking.
——
2200 J/kg.K
Gasoline, or petrol is a clear petroleum-derived flammable liquid. Currently, the main source of fuel for road vehicles is petroleum oil.
Gasoline is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines. The usage and pricing of gasoline (or petrol) results from factors such as crude oil prices, processing and distribution costs, local demand, the strength of local currencies, local taxation, and the availability of local sources of gasoline (supply). Since fuels are traded worldwide, the trade prices are similar.
——
2100 J/kg.K
In general, diesel fuel is any liquid fuel specifically designed for use in diesel engines, whose fuel ignition takes place, without any spark, as a result of compression of the inlet air mixture and then injection of fuel. Currently, the main source of fuel for road vehicles is petroleum oil.
Gasoline is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines. The usage and pricing of gasoline (or petrol) results from factors such as crude oil prices, processing and distribution costs, local demand, the strength of local currencies, local taxation, and the availability of local sources of gasoline (supply).
——
1674 J/kg.K
Acetylene is a colorless, highly flammable gas with an ethereal odor. Acetylene is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne with the formula C2H2. Commercial acetylene will have a garlic-like odor. It is shipped with dissolved acetone in its gaseous form.
Typical uses oxyacetylene chemical synthesis and especially for welding and cutting. Among all other gases, acetylene is capable of producing the hottest flame. The welding process that uses acetylene is known as oxy-fuel cutting or gas cutting.
Specific Heat Capacity of Materials
Specific heat, or specific heat capacity, is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics. The intensive properties cv and cp are defined for pure, simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of the internal energy u(T, v) and enthalpy h(T, p), respectively:
 where the subscripts v and p denote the variables held fixed during differentiation. The properties cv and cp are referred to as specific heats (or heat capacities) because under certain special conditions they relate the temperature change of a system to the amount of energy added by heat transfer. Their SI units are J/kg K or J/mol K.
where the subscripts v and p denote the variables held fixed during differentiation. The properties cv and cp are referred to as specific heats (or heat capacities) because under certain special conditions they relate the temperature change of a system to the amount of energy added by heat transfer. Their SI units are J/kg K or J/mol K.
Different substances are affected to different magnitudes by the addition of heat. When a given amount of heat is added to different substances, their temperatures increase by different amounts.
Heat capacity is an extensive property of matter, meaning it is proportional to the size of the system. Heat capacity C has the unit of energy per degree or energy per kelvin. When expressing the same phenomenon as an intensive property, the heat capacity is divided by the amount of substance, mass, or volume, thus the quantity is independent of the size or extent of the sample.