About Strontium
Strontium is an alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically.
Summary
| Element | Strontium |
| Atomic number | 38 |
| Element category | Alkaline Earth Metal |
| Phase at STP | Solid |
| Density | 2.63 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | N/A |
| Yield Strength | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus of Elasticity | 15.7 GPa |
| Mohs Scale | 1.8 |
| Brinell Hardness | N/A |
| Vickers Hardness | N/A |
| Melting Point | 777 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1382 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35.3 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 22.5 µm/mK |
| Specific Heat | 0.3 J/g K |
| Heat of Fusion | 8.3 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 144 kJ/mol |
| Electrical resistivity [nanoOhm meter] | 132 |
| Magnetic Susceptibility | −92e-6 cm^3/mol |
Applications of Strontium
Consuming 75% of production, the primary use for strontium was in glass for colour television cathode ray tubes. Strontium is best known for the brilliant reds its salts give to fireworks and flares. It is also used in producing ferrite magnets and refining zinc. Modern ‘glow-in-the-dark’ paints and plastics contain strontium aluminate. They absorb light during the day and release it slowly for hours afterwards. The isotope Sr90 has a half-life of 28 years and is one of the well-known high-energy beta emitters. Hence, it is employed in systems for nuclear auxiliary power (SNAP) devices, which find potential applications in remote weather stations, space vehicles, navigational buoys, etc.
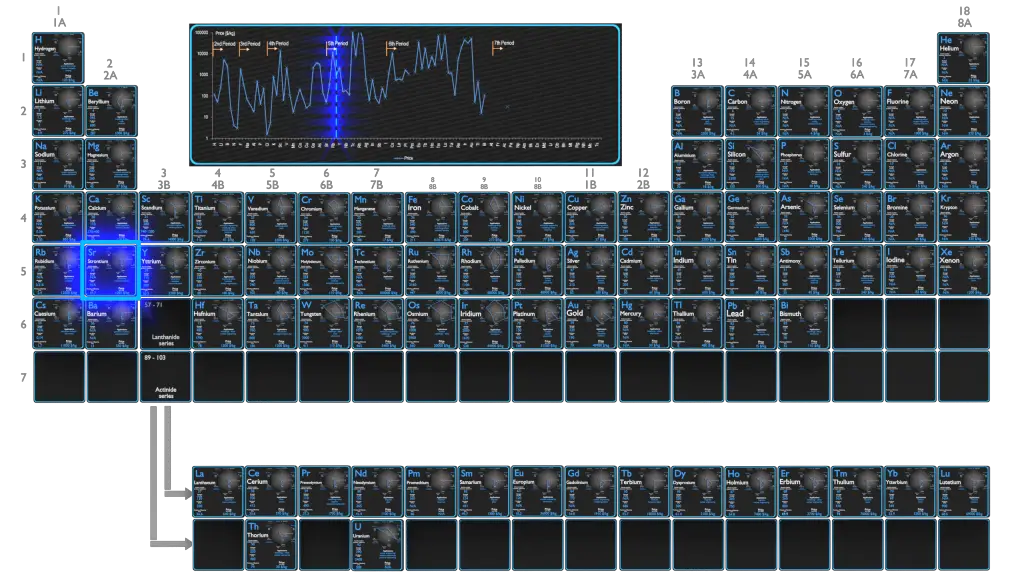
Production and Price of Strontium
Raw materials prices change daily. They are primarily driven by supply, demand and energy prices. In 2019, prices of pure Strontium were at around 1000 $/kg.
The three major producers of strontium as celestine as of 2015 are China (150,000 t), Spain (90,000 t), and Mexico (70,000 t); Argentina (10,000 t) and Morocco (2,500 t) are smaller producers. A large proportion of mined celestine (SrSO4) is converted to the carbonate by two processes. Either the celestine is directly leached with sodium carbonate solution or the celestine is roasted with coal to form the sulfide.
Source: www.luciteria.com
Mechanical Properties of Strontium
Strength of Strontium
In mechanics of materials, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. Strength of materials basically considers the relationship between the external loads applied to a material and the resulting deformation or change in material dimensions. In designing structures and machines, it is important to consider these factors, in order that the material selected will have adequate strength to resist applied loads or forces and retain its original shape. Strength of a material is its ability to withstand this applied load without failure or plastic deformation.
For tensile stress, the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to elongate is known as ultimate tensile strength (UTS). Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins.
See also: Strength of Materials
Ultimate Tensile Strength of Strontium
Ultimate tensile strength of Strontium is N/A.
Yield Strength of Strontium
Yield strength of Strontium is N/A.
Modulus of Elasticity of Strontium
The Young’s modulus of elasticity of Strontium is N/A.
Hardness of Strontium
In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation (localized plastic deformation) and scratching. Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested.
Brinell hardness of Strontium is approximately N/A.
The Vickers hardness test method was developed by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers hardness test method can be also used as a microhardness test method, which is mostly used for small parts, thin sections, or case depth work.
Vickers hardness of Strontium is approximately N/A.
Scratch hardness is the measure of how resistant a sample is to permanent plastic deformation due to friction from a sharp object. The most common scale for this qualitative test is Mohs scale, which is used in mineralogy. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is based on the ability of one natural sample of mineral to scratch another mineral visibly.
Strontium is has a hardness of approximately 1.8.
See also: Hardness of Materials
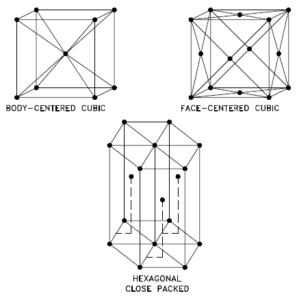
Strontium – Crystal Structure
A possible crystal structure of Strontium is face-centered cubic structure.
In metals, and in many other solids, the atoms are arranged in regular arrays called crystals. A crystal lattice is a repeating pattern of mathematical points that extends throughout space. The forces of chemical bonding causes this repetition. It is this repeated pattern which control properties like strength, ductility, density, conductivity (property of conducting or transmitting heat, electricity, etc.), and shape. There are 14 general types of such patterns known as Bravais lattices.
See also: Crystal Structure of Materials
Crystal Structure of Strontium
Thermal Properties of Strontium
Strontium – Melting Point and Boiling Point
Melting point of Strontium is 777°C.
Boiling point of Strontium is 1382°C.
Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure.
Strontium – Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity of Strontium is 35.3 W/(m·K).
The heat transfer characteristics of a solid material are measured by a property called the thermal conductivity, k (or λ), measured in W/m.K. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to transfer heat through a material by conduction. Note that Fourier’s law applies for all matter, regardless of its state (solid, liquid, or gas), therefore, it is also defined for liquids and gases.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Strontium
Linear thermal expansion coefficient of Strontium is 22.5 µm/(m·K)
Thermal expansion is generally the tendency of matter to change its dimensions in response to a change in temperature. It is usually expressed as a fractional change in length or volume per unit temperature change.
Strontium – Specific Heat, Latent Heat of Fusion, Latent Heat of Vaporization
Specific heat of Strontium is 0.3 J/g K.
Heat capacity is an extensive property of matter, meaning it is proportional to the size of the system. Heat capacity C has the unit of energy per degree or energy per kelvin. When expressing the same phenomenon as an intensive property, the heat capacity is divided by the amount of substance, mass, or volume, thus the quantity is independent of the size or extent of the sample.
Latent Heat of Fusion of Strontium is 8.3 kJ/mol.
Latent Heat of Vaporization of Strontium is 144 kJ/mol.
Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a change in phase. This energy breaks down the intermolecular attractive forces, and also must provide the energy necessary to expand the gas (the pΔV work). When latent heat is added, no temperature change occurs. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place.
Strontium – Electrical Resistivity – Magnetic Susceptibility
Electrical property refers to the response of a material to an applied electric field. One of the principal characteristics of materials is their ability (or lack of ability) to conduct electrical current. Indeed, materials are classified by this property, that is, they are divided into conductors, semiconductors, and nonconductors.
See also: Electrical Properties
Magnetic property refers to the response of a material to an applied magnetic field. The macroscopic magnetic properties of a material are a consequence of interactions between an external magnetic field and the magnetic dipole moments of the constituent atoms. Different materials react to the application of magnetic field differently.
See also: Magnetic Properties
Electrical Resistivity of Strontium
Electrical resistivity of Strontium is 132 nΩ⋅m.
Electrical conductivity and its converse, electrical resistivity, is a fundamental property of a material that quantifies how Strontium conducts the flow of electric current. Electrical conductivity or specific conductance is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity.
Magnetic Susceptibility of Strontium
Magnetic susceptibility of Strontium is −92e-6 cm^3/mol.
In electromagnetism, magnetic susceptibility is the measure of the magnetization of a substance. Magnetic susceptibility is a dimensionless proportionality factor that indicates the degree of magnetization of Strontium in response to an applied magnetic field.